
UG Module 4 - Lesson 3
VAMANA KARMA
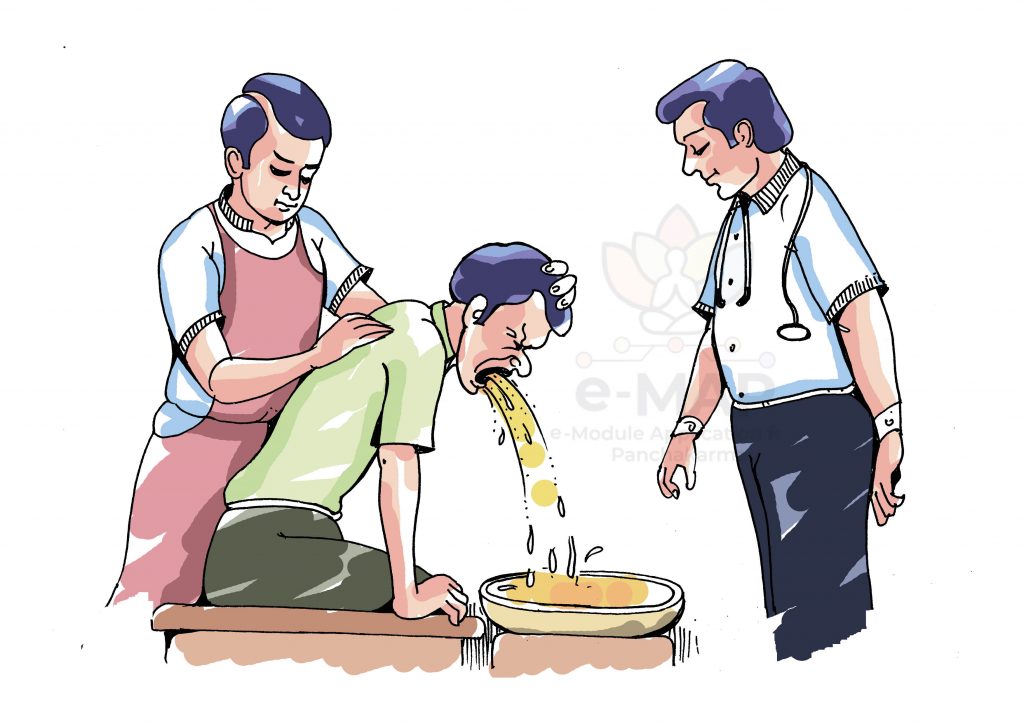
EXPLANATORY NOTES
Vamana Dravyas
फलजीमूतकेक्ष्वाकुकल्पो धामार्गवस्य च||
पञ्चमो वत्सकस्योक्तः षष्ठश्च कृतवेधने| (Cha. Su. 30/62)
According to Ācārya Caraka, Vamana drugs are Madanaphala (Randia dumetorum), Jīmūta (Luffa echinata), Ikṣvāku (Lagenaria vulgaris), Dhāmārgava (Luffa cylindrica), Vatsaka (Holarrehena antidysentrica), Kṛtavedana (Luffa acutangula)
मदनमधुकलम्बानिम्बबिम्बीविशाला–
त्रपुसकुटजमूर्वादेवदालीकृमिघ्नम्|
विदुलदहनचित्राः कोशवत्यौ करञ्जः
कणलवणवचैलासर्षपाश्र्छर्दनानि|| (A. H. Su. 15/1)
The drugs mentioned in Vamana Dravya Gaṇa explained by Ācārya Vāgbhaṭa are Madanaphala (Randia dumetorum), Madhuka (Glycyrrhiza glabra), Lamba (Lagenaria siceraria), Nimba (Azadirachta indica), Bimbi (Coccinia indica), Viśāla (Citrullus colocynthis), Trapusa (Cucumis sativus), Kutaja (Holarrhina antidysenterica), Mūrva (Marsdenia tenacissima), Devatāli (Luffa echinata), Krmighna (Embelia ribes), Vidula (Barringtonia acutangula), Dahana (Plumbago zeylanica), Citra (Trichosanthes anguina), 2 types of Kośavati – Kośātaki (Luffa acutangula) and Dhāmārgava (Luffa cylindrica), Karañja (Pongamia pinnata), Kaṇa (Piper longum), Lavaṇa (salt), Vacā (Acorus calamus), Ela (Elettaria cardamomum), Sarśapa (Brassica campestris)
Vamana Upaga Dravyas
मधुमधुककोविदारकर्बुदारनीपविदुलबिम्बीशणपुष्पीसदापुष्पाप्रत्यक्पुष्पा इति दशेमानि वमनोपगानि भवन्ति || (Cha. Su. 4/13)
The 10 Vamanopaga Dravyas Mentioned By Ācārya Caraka are Madhu (Honey), Madhuka (Glycyrrhiza glabra), Kovidāra (Bauhinia purpurea), Karbudāra (Bauhinia Variegata), Nīpa (Anthocephalus cadamba), Vidula (Barringtonia acutangula), Bimbi (Coccinia indica), Śaṇapuṣpī (Crotalaria verrucose), Sadāpuṣpi (Calotropis gigantea), Pratyakpuṣpī (Achyranthes aspera).
Vamana Dravyas | |||||
Rasa | Guna | Vīrya | Vipāka | Karma | |
Madanaphala (Randia dumetorum) | Madhura, Tikta | Rūkṣa, Laghu | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Kaphapittahara, Vātanulomana, Āśukāri Anapayatvam |
Jīmūta (Luffa echinata) | Kaṭu Tikta | Laghu Rūkṣa | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Tridoṣaghna |
Ikṣvāku (Lagenaria vulgaris) | Tikta | Laghu Rūkṣa | Śīta | Kaṭu | Kaphapittahara |
Dhāmārgava (Luff cylindrica) | Tikta | Laghu Rūkṣa Tīkṣṇa | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Kaphapittahara |
Vatsaka (Holarrehena antidysentrica) | Tikta Kaṣāya | Laghu Rūkṣa | Śīta | Kaṭu | Kaphapittahara |
Kṛtavedana (Luffa acutangula) | Tikta | Laghu Rūkṣa Tīkṣṇa | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Kaphapittahara |
Vamanopaga Dravyas | |||||
Madhuka (Glycyrrhiza glabra) | Madhura | Guru Snigdha | Śīta | Madhura | Tridoṣahara Rasāyana Vrṣya |
Kovidāra (Bauhinia purpurea) | Kaṣāya | Rūkṣa Laghu | Śīta | Kaṭu | Pittahara |
Karbudāra (Bauhinia variegata) | Kaṣāya | Rūkṣa Laghu | Śīta | Kaṭu | Kapha Pittahara |
Nīpa (Anthocephalus cadamba) | Madhura Kaṣāya Lavaṇa | Guru Rūkṣa | Śīta | Kaṭu | Vāta Kaphahara |
Vidula (Barringtonia acutangula) | Tikta Kaṭu | Laghu Rūkṣa | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Kapha Vātahara |
Bimbi (Coccinia indica) | Tikta | Laghu Rūkṣa Tīkṣṇa | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Kapha Pittahara |
Śaṇapuṣpī (Crotalaria verrucosa) | Tikta, Kaṭu, Kaṣāya | Laghu Rūkṣa Tīkṣṇa | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Kapha Pitta Doṣas |
Sadāpuṣpi (Calotropis gigantea) | Kaṭu Tikta | Laghu Rūkṣa Tīkṣṇa | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Kaphahara |
Pratyak Puṣpi (Achyranthes aspera) | Kaṭu Tikta | Laghu Rūkṣa Tīkṣṇa | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Kapha Vātahara |
Vacā (Acorus calamus) | Tikta Kaṭu | Uṣṇa Tīkṣṇa | Uṣṇa | Kaṭu | Vātanulomaka Śakṛtmūtra Viśodhini Śūlaghni |
Nimba (Azadiracta indica) | Tikta Kaṣāya | Laghu Rūkṣa | Śīta | Kaṭu | Dīpana Kaphapittahara Kṛmighna |
Introduction
In Caraka Saṁhita Kalpasthāna 133 Yōgās of Madanaphala are mentioned. The drug Madanaphala is differing from other Vāmaka Auṣadhi by its unique Rasapañcaka, method of collection and processing (Saṁskaraṇa).
नव योगाः कषायेषु, मात्रास्वष्टौ , पयोघृते|
पञ्च, फाणितचूर्णे द्वौ घ्रेये, वर्तिक्रियासु षट्||
विंशतिर्विंशतिर्लेहमोदकोत्कारिकासु च|
शष्कुलीपूपयोश्चोक्ता योगाः षोडश षोडश||
दशान्ये षाडवाद्येषु त्रयस्त्रिंशदिदं शतम्|
योगानां विधिवद्दिष्टं फलकल्पे महर्षिणा|| (Cha. Ka. 1/30)
Nine recipes of Madanaphala in the form of decoction, eight recipes of Madanaphala Mātrā, Five Madanaphala Kṣīra and Ghṛta Yogas, two in Phāṇita and Cūrṇa, one in inhalation, six in Varti, twenty each in Leha, Modaka and Utkārikā, sixteen each in Śaṣkuli and Pūpa and ten others in Ṣāḍava etc. Thus total 133 formulations were detailed by great sages in this Adhyāya.
Definition of Vamana and Virecana
तत्र दोषहरणमूर्ध्वभागं वमनसञ्ज्ञकम्, अधोभागं विरेचनसञ्ज्ञकम्; उभयं वा शरीरमलविरेचनाद्विरेचनसञ्ज्ञां लभते| (Cha. Ka. 1/4)
Vamana Karma is a procedure which is indicated in Kapha Pravr̥ddha Avasthā. It defines as the forceful expulsion of Apakva Pitta and Ślēṣma through the upper GIT orifice. The expelling of morbid materials through the downward tract is called as Virecana. Since they expel vitiated Dośas from the body both these procedures are also called Virecana.
Mode of action of Vamana and Virecana
तत्रोष्णतीक्ष्णसूक्ष्मव्यवायिविकाशीन्यौषधानि स्ववीर्येण हृदयमुपेत्य धमनीरनुसृत्य स्थूलाणुस्रोतोभ्यः केवलं शरीरगतं दोषसङ्घातमाग्नेयत्वाद् विष्यन्दयन्ति, तैक्ष्ण्याद् विच्छिन्दन्ति, स विच्छिन्नः परिप्लवन् स्नेहभाविते काये स्नेहाक्तभाजनस्थमिव क्षौद्रमसज्जन्नणुप्रवणभावादामाशयमागम्योदानप्रणुन्नोऽग्निवाय्वात्मकत्वादूर्ध्वभागप्रभावादौषधस्योर्ध्वमुत्क्षिप्यते, सलिलपृथिव्यात्मकत्वादधोभागप्रभावाच्चौषधस्याधः प्रवर्तते, उभयतश्चोभयगुणत्वात्| इति लक्षणोद्देशः|| (Cha. Ka. 1/5)
Vāmaka Dravyās are Uṣna, Tikṣna, Sukṣma, Vyavāyi, Vikāshi in nature. By the Vīrya/ potency of the drug, it reaches Hṛdaya and later circulates through the blood vessels. Due to the predominance of Agni Mahābhūta, the drug possesses Āgneya nature. Because of their Tikṣna Guna, they liquefy the adhered Dośas in the gross and subtle channels of the body. After separation these morbid materials floats in the body channels without adhesion like how honey kept in a pot smeared with fat, the morbid materials finally reaches the stomach. By the predominance of Agni and Vāyu Mahābhūta and their Vāmaka Prabhāva (specific action to move upward), the morbid materials gets propelled by Udāna Vāyu through the upward tract
Types of Deśa
त्रिविधः खलु देशः– जाङ्गलः, आनूपः, साधारणश्चेति| (Cha. Ka. 1/8)
Habitat are of three types: Jāṅgala (Dry land), Anūpa (Marshy Land), and Sādhāraṇa Deśa (Normal Land).
Jāṅgala Deśa:
तत्र जाङ्गलः पर्याकाशभूयिष्ठः, तरुभिरपि च कदर–खदिरासनाश्वकर्ण–धव–तिनिश–शल्लकी–साल–सोमवल्क–बदरी–तिन्दुकाश्वत्थ–वटामलकीवनगहनः, अनेकशमी–ककुभ–शिंशपाप्रायः, स्थिरशुष्कपवनबलविधूयमानप्रनृत्यत्तरुणविटपः, प्रततमृगतृष्णिकोपगूढतनुखरपरुषसिकताशर्कराबहुलः, लावतित्तिरिचकोरानुचरितभूमिभागः, वातपित्तबहुलः, स्थिरकठिनमनुष्यप्रायो ज्ञेयः
(Cha. Ka. 1/8)
It abounds in open sky. It has deep forests of trees like Kadara, Khadira, Asana, Śallakī, Aśvakarṇa, Dhava, Tiniśa, Śallakī, Śālā, Somavalkā, Badarī, Tinduka, Aśvatha, Vāta, Āmalaka. It is surrounded by trees of Śami, Kakubha, and Śiṃśapā in large number.
The tender branches of these trees being swayed by continuous dry wind. It is largely covered by dry and rough sands as well as gravels which give rise to mirages. This area is inhabited by the birds like Lāva, Tittiri and Cakora. The people inhabiting this type of land are dominated by Vāyu and Pitta and most of them are sturdy and hard
Anūpa Deśa:
अथानूपो हिन्तालतमालनारिकेलकदलीवनगहनः, सरित्समुद्रपर्यन्तप्रायः, शिशिरपवनबहुलः, वञ्जुलवानीरोपशोभिततीराभिः सरिद्भिरुपगतभूमिभागः, क्षितिधरनिकुञ्जोपशोभितः, मन्दपवनानुवीजितक्षितिरुहगहनः, अनेकवनराजीपुष्पितवनगहनभूमिभागः, स्निग्धतरुप्रतानोपगूढः, हंस–चक्रवाक–बलाका–नन्दीमुख–पुण्डरीक–कादम्ब–मद्गु [१] –भृङ्गराज–शतपत्र मत्तकोकिलानुनादिततरुविटपः, सुकुमारपुरुषः, पवनकफप्रायो ज्ञेयः;
(Cha. Ka. 1/8)
It contains deep forests of trees like Hintāla, Tamāla, Nārikela and Kadalī. It is located generally at the banks of rivers and sea and banks were beautified by plants like Vañjulā and Vānīra. It has mountains covered with beautiful creepers. The trees in this thick forest wave with the gentle breeze. The area is surrounded by thick forest with beautiful and blossoming trees. The branches of trees located here are echoed with the sound produced by birds like Haṃsa, Cakravāka, Bālaka, Nandīmukha, Madgu & inebriated by Kokila. People inhabiting this type of land are of tender body and generally they are dominated by Vāyu & Kapha.
Sādhāraṇa Deśa:
अनयोरेव द्वयोर्देशयोर्वीरुद्वनस्पतिवानस्पत्यशकुनिमृगगणयुतः स्थिरसुकुमारबलवर्णसंहननोपपन्नसाधारणगुणयुक्तपुरुषः साधारणो ज्ञेयः| (Cha. Ka. 1/8)
It has creepers, Vanaspati (~trees having fruits without apparent flowers), Vānaspatya (~trees having both fruits & flowers), birds and beasts described above in respect of Jāṅgala and Anūpadeśa.
Persons inhabiting this land are sturdy, tender, endowed with strength, complexion and compactness, as well as other attributes of people inhabiting in the land of general nature.
Deśa, Kāla and method of drug collection
Appropriate Deśa
तत्र देशे साधारणे जाङ्गले वा यथाकालं शिशिरातपपवनसलिलसेविते
समे शुचौ प्रदक्षिणोदके श्मशान–चैत्य–देवयजनागार–सभा–श्वभ्राराम–वल्मीकोषरविरहिते कुशरोहिषास्तीर्णे स्निग्धकृष्णमधुरमृत्तिके सुवर्णवर्णमधुरमृत्तिके
वा मृदावफालकृष्टेऽनुपहतेऽन्यैर्बलवत्तरैर्द्रुमैरौषधानि जातानि प्रशस्यन्ते||
(Cha. Ka. 1/9)
Time and Method of collection
तत्र यानि कालजातान्युपागतसम्पूर्णप्रमाण–रसवीर्य–गन्धानि
कालातपाग्निसलिलपवनजन्तुभिरनुपहतगन्ध–
वर्ण–रस–स्पर्श–प्रभावाणि प्रत्यग्राण्युदीच्यां दिशि स्थितानि;
तेषां शाखापलाशमचिरप्ररूढं वर्षावसन्तयोर्ग्राह्यं, ग्रीष्मे मूलानि
शिशिरे वा शीर्णप्ररूढपर्णानां, शरदि त्वक्कन्दक्षीराणि,
हेमन्ते साराणि, यथर्तु पुष्पफलमिति; मङ्गलाचारः कल्याणवृत्तः शुचिः
शुक्लवासाः सम्पूज्य देवता अश्विनौ गोब्राह्मणांश्च कृतोपवासः
प्राङ्मुख उदङ्मुखो वा गृह्णीयात्|| (Cha. Ka. 1/10)
Proper Storage
गृहीत्वा चानुरूपगुणवद्भाजनस्थान्यागारेषू प्रागुदग्द्वारेषु निवातप्रवातैकदेशेषु
नित्यपुष्पोपहारबलिकर्मवत्सु, अग्नि–सलिलोपस्वेद–धूम–रजो–मूषक चतुष्पदामनभिगमनीयानि स्ववच्छन्नानि शिक्येष्वासज्य स्थापयेत्|| (Cha. Ka. 1/11)
Deśa | Time and Method of collection. | Storage |
Sādhāraṇa and Jāṅgala Deśa are Śreṣṭha. | Śākhā and Pallava (tender branches and leaves): Varśa Ṛtu. | The Storage room should face east or north direction. |
Plants should expose to seasonal cold, wind, sunrays, rain. | Mūla(roots): Grīṣma, Late Śiśira Ṛtu | It should be devoid of excess wind, fire, moisture, smoke, dust, mice, quadrupeds. |
Plants that grow in clean land surrounded by water reservoirs are excellent therapeutic efficacy. | Tvak (bark), Kanda (rhizome), Kṣīra (latex) : Śarat Ṛtu | It should be equipped with appropriate containers and lids. |
The land should be devoid of big trees, crematorium, prayer ground, parks, ant hills, saline soil. | Sāra (heart wood) : Hemanta Ṛtu | Daily perform flower offerings and sacrificial rituals. |
Land with soil having Guṇas like Snigdha, Madhura Rasa, Svarṇa / Kṛṣṇa (black) Varṇa are preferred. Land which have enormous growth of Kuśa and Rohiṣa are also Śreṣṭha. | Flowers and Fruits: Yadhā Ṛtu(On Appropriate Season) | Pravāta: Eka Deśeshu There should be only one window for ventilation. |
ANŪPANA
तानि च यथादोषं प्रयुञ्जीत सुरा–सौवीरक–तुषोदक–मैरेय–मेदक–धान्याम्ल [१] –फलाम्ल–दध्यम्लादिभिर्वाते, मृद्वीकामलक –मधु–मधुक–परूषक–फाणितक्षीरादिभिः
पित्ते, श्लेष्मणि तु मधु–मूत्र–कषायादिभिर्भावितान्यालोडितानि च; इत्युद्देशः|
तं विस्तरेण द्रव्य–देह–दोष–सात्म्यादीनि प्रविभज्य व्याख्यास्यामः||
(Cha. Ka.1/12)
The adjuvants according to the Dośas are detailed in this Adhyāya. The Auṣadhis (drugs)can be impregnated or mixed with these adjuvants for better efficacy.
Dośa | Anūpana |
Vāta | Surā, Sauvīraka, Tuṣodaka, Maireyaka, Medaka, Dhānyāmla, Dadhyamla, Phalāmla |
Pitta | Mrdvīka, Āmalaka, Madhu, Madhūka, Parūṣaka, Phāṇita, Kṣīra. |
Kapha | Madhu, Mūtra, Kaṣāya |
Madanaphala collection
वमनद्रव्याणां मदनफलानि श्रेष्ठतमान्याचक्षते, अनपायित्वात्|
तानि वसन्तग्रीष्मयोरन्तरे पुष्याश्वयुग्भ्यां मृगशिरसा वा गृह्णीयान्मैत्रे मुहूर्ते|
यानि पक्वान्यकाणान्यहरितानि पाण्डून्यक्रिमीण्यपूतीन्यजन्तुजग्धान्यह्रस्वानि; तानि प्रमृज्य ,
कुशपुटे बद्ध्वा, गोमयेनालिप्य, यवतु(बु)षमाषशालिकुलत्थमुद्गपलानामन्यतमे निदध्यादष्टरात्रम्|
अत ऊर्ध्वं मृदूभूतानि मध्विष्टगन्धान्युद्धृत्य शोषयेत्|
सुशुष्काणां फलपिप्पलीरुद्धरेत् तासां घृतदधिमधुपललविमृदितानां
पुनः शुष्काणां नवं कलशं सुप्रमृष्टवालुकमरजस्कमाकण्ठं पूरयित्वा
स्ववच्छन्नं स्वनुगुप्तं शिक्येष्वासज्य सम्यक् स्थापयेत्|| (Cha. Ka. 1/13)
Due to Anapāyitva (less complication) it is Śrēṣṭa among Vāmaka Dravyās. It should be collected between Vasanta (spring) and Grīṣma (summer) Ṛtus (seasons), in Puṣyā, Aśvinī and Mrgaśīrṣa Nakśatra (when the moon is in these three constellation) during the Maitreya Muhūrta (auspicious period of the day). The fruit should be Pakva (fully matured), Akana (not perforated), Aharita (not greenish in colour), Pāndu Varṇa (should be yellowish white in colour), Akrmi (without insects), Apūti (without bad smell), Ajantu Jagdha (not infested by parasites), Ahrasva (not small in size). Such fruits should be cleaned, tied in Kuśa (bundle of Kuśa grass) and Gomaya Lepa (application of cow dung paste) should be done. Then it is kept in either of Yava (barley husk), Tuśa, Māśa, Sāli, Kulatha or Mudga Rāshi for eight nights. It should be then removed from rāshi which will be Mṛdu (soft), endowed with Madhvishta Gandha (desirable smell like that of honey). After drying the Phalapippali (seeds) are removed and Mardana (tṚturation) is done with Ghṛta (ghee), Dadhi (curds), Madhu (honey) and Palala (oil-cake). Again, it (Samskārita Madanapippali) is kept for drying which is later stored in a Nava Kalaśa (new earthen pot/jar) which is well cleaned from inside and filled up to Ākantastha (brim) then covered with a lid.
Synonyms of Madanaphala
मदनः करहाटश्च राठः पिण्डीतकः फलम्|
श्वसनश्चेति पर्यायैरुच्यते तस्य कल्पना|| (Cha. Ka. 1/27)
Madana, Karahāta, Rāṭa , Piṇḍītaka, Phala and Śvasana are the synonyms of Madanaphala.
Vamana vidhi
अथ च्छर्दनीयमातुरं द्व्यहं त्र्यहं वा स्नेहस्वेदोपपन्नं श्वश्छर्दयितव्यमिति
ग्राम्यानूपौदकमांसरस–क्षीर–दधि–माष–तिल–शाकादिभिः समुत्क्लेशितश्लेष्माणं व्युषितं
जीर्णाहारं पूर्वाह्णे कृतबलिहोममङ्गलप्रायश्चित्तं निरन्नमनतिस्निग्धं यवाग्वा घृतमात्रां पीतवन्तं,
तासां फलपिप्पलीनामन्तर्नखमुष्टिं यावद्वा साधु मन्येत जर्जरीकृत्य यष्टिमधुकषायेण कोविदार–कर्बुदार–नीप–विदुल–बिम्बी–शणपुष्पी–सदापुष्पी–प्रत्यक्पुष्पी–कषायाणामन्यतमेन वा रात्रिमुषितं विमृद्य पूतं
मधुसैन्धवयुक्तं सुखोष्णं कृत्वा पूर्णं शरावं मन्त्रेणानेनाभिमन्त्रयेत्–
(Cha. Ka. 1/14)
Before Vamana the patient should undergo Śodhanānga Snehana and Svedana for two or three days. During the night before the day of administration of the emetic therapy he should intake Kaphothkleśakara Aharas like Māṃsarasa prepared out of Grāmya, Anūpa and Audaka Māṃsa, Kṣīra, Dadhi, Māṣa, sesamum seeds, vegetables (Sāka). In the next morning after accessing the Jīrna Āhāra Lakśana and offering the prayers, the Snigdha Yavāgu can be given to the patient. The Madanaphala in Antarnakha Muṣṭi Pramāṇa can be taken and processed with any of the decoctions of Yashtimadhu, Kovidāra, Karbudāra, Nīpa, Vidula, Bimbī, Śaṇapuṣpī, Prathyakpuṣpī and kept overnight. In the morning this should be stirred with hand and filtered. The liquid thus obtained should be added with honey, rock salt, made slightly warm, filled up to the brim in a drinking pot and administered to the patient with the following mantra.
‘ॐ ब्रह्मदक्षाश्विरुद्रेन्द्रभूचन्द्रार्कानिलानलाः|
ऋषयः सौषधिग्रामा भूतसङ्घाश्च पान्तु ते|
रसायनमिवर्षीणां देवानाममृतं यथा|
सुधेवोत्तमनागानां भैषज्यमिदमस्तु ते’|
इत्येवमभिमन्त्र्योदङ्मुखं प्राङ्मुखं वाऽऽतुरं पाययेच्छ्लेष्मज्वरगुल्मप्रतिश्यायार्तं
विशेषेण पुनः पुनरापित्तागमनात्, तेन साधु वमति; हीनवेगं तु पिप्पल्यामलक–सर्षप–वचाकल्कलवणोष्णोदकैः पुनः पुनः प्रवर्तयेदापित्तदर्शनात्|
इत्येष सर्वश्छर्दनयोगविधिः|| (Cha. Ka. 1/14)
The patient should face east or north direction and consume the Vamana Auśadhi. Till the pitta Darśana in the vomited material, the procedure will continue. Vamana is indicated in Kaphaja Jvara, Pratishyāya and Gulam. If the Vamana Vegas are not proper, then the Auśadhi should be augmented by the repeated administration of the Kalka of Pippali, Āmalaka, Vācā, Sarśapa and Saindhava along with luke warm water.
Importance of Madhu and Saindhava
सर्वेषु तु मधुसैन्धवं कफविलयनच्छेदार्थं वमनेषु विदध्यात्|
न चोष्णविरोधो मधुनश्छर्दनयोगयुक्तस्य, अविपक्वप्रत्यागमनाद्दोषनिर्हरणाच्च|| (Cha. Ka. 1/15)
In all the Vāmaka Auśadhi, Madhu and Saindhava should be added, to enhance the Kapha Vilayana (liquefaction) and Kapha Chedhanartham (separate adhered Kapha). As this Madhu is not undergoing the Pāka (digestion) during Vamana and expelled along with the vitiated Dośas it will not produce any adverse effect.
Madanaphala Mātrāyogam (Pills)
फलपिप्पलीनां द्वौ द्वौ भागौ कोविदारादिकषायेण त्रिःसप्तकृत्वः स्रावयेत्, तेन रसेन तृतीयं भागं पिष्ट्वा मात्रां हरीतकीभिर्बिभीतकैरामलैर्वा तुल्यां वर्तयेत्, तासामेकां द्वे वा पूर्वोक्तानां कषायाणामन्यतमस्याञ्जलिमात्रेण विमृद्य बलवच्छ्लेष्मप्रसेकग्रन्थिज्वरोदरारुचिषु पाययेदिति समानं पूर्वेण|| (Cha. Ka. 1/16)
Two parts of the seeds of Madanaphala added with six parts of decoction of any of the drugs Kovidāra, Karbudāra, Nīpa, Vidula, Bimbī, Śaṇapuṣpī, Sadāpuṣpī or Prathyakpuṣpī, then strained for 21 times. Along with this liquid one part of Madanaphala seed is triturated and Kalka is obtained. Out of this Madanaphala Kalka pills with a size of Harītaki, Vibhītaki or Āmalaka is prepared. In the conditions like Praseka, Granti, Jvara, Udara and Aruci one /two Madanaphala pills along with the decoction of any of the drugs Kovidāra, Karbudāra, Nīpa, Vidula, Bimbī, Śaṇapuṣpī, Sadāpuṣpī or Prathyakpuṣpī can administer.
MADANAPHALA KṢĪRA YOGAS
फलपिप्पलीक्षीरं, तेन वा क्षीरयवागूमधोभागे रक्तपित्ते हृद्दाहे च; तज्जस्य वा दध्न उत्तरकं कफच्छर्दितमकप्रसेकेषु तस्य वा पयसः शीतस्य सन्तानिकाञ्जलिं पित्ते प्रकुपिते उरःकण्ठहृदये च तनुकफोपदिग्धे, इति समानं पूर्वेण|| (Cha. Ka. 1/17)
1) In Adhoga Rakthapitta and Hṛtdāha: Madanaphala Pippali Siddha Kṣīra / Kṣīra peya
2)In Kaphaja Cardhi, Praseka, Tamaka Śvāsa: Dadhi Utharaka (Cream of yoghurt) out of Madanaphala Pippali Siddha Kṣīra
3) In Pitta Prakopa, and when chest, throat and heart are affected with thin layer of Kapha:
Santhana Kalpana (cream of milk) in one Añjali Pramāṇa can be administer to the patient.
MADANAPHALA GHṚTA YOGAS
फलपिप्पलीशृतक्षीरान्नवनीतमुत्पन्नं फलादिकल्ककषायसिद्धं कफाभिभूताग्निं विशुष्यद्देहं च मात्रया पाययेदिति समानं पूर्वेण|| (Cha. Ka. 1/18)
The Navanīta prepared out of Madanaphala Pippali Siddha Kṣīra processed with Kalka and Kaṣāya of the Auśadhis like Madanaphala, Jīmūthaka, Ikṣvāku, Dhāmārgava, Kutaja and Krtavedana. Phala Pippali Śṛta Ksīrannavanīta Utpanna Ghṛta (ghee obtained from butter collected from milk) can be administered to the patients suffering from suppression of Agni by Kapha and Śuṣyadeha (dehydration of the body).
MADANAPHALA GHṚEYA YOGA (INHALATION)
फलपिप्पलीनां फलादिकषायेण त्रिःसप्तकृत्वः सुपरिभावितेन पुष्परजःप्रकाशेन चूर्णेन सरसि सञ्जातं बृहत्सरोरुहं सायाह्नेऽवचूर्णयेत्, तद्रात्रिव्युषितं प्रभाते पुनरवचूर्णितमुद्धृत्य हरिद्राकृसरक्षीरयवागूनामन्यतमं सैन्धवगुडफाणितयुक्तमाकण्ठं पीतवन्तमाघ्रापयेत् सुकुमारमुत्क्लिष्टपित्तकफमौषधद्वेषिणमिति समानं पूर्वेण|| (Cha. Ka.1/19)
For Ghṛeya Yoga the seeds of Madanaphala undergone Bhāvana with the decoction of Jīmūthaka, Ikṣvāku, Dhāmārgava, Kutaja and Krtavedana for 21 times and made into fine powder. Later in the evening the power of Madanapippali were sprinkled over the lotus and kept overnight. On next day morning the powder is collected and administered for inhalation to induce Vamana. Gherya Yoga is mainly indicated for Sukumāra, Pitta and Kapha Utkliṣṭa Avasthā, and for Auṣadha Dveshina (those have aversion to take medicine orally). Before Ghṛeya Yoga administration Ākantapana with Haridra Krsara, Kṣīra Yavāgu along with Phānitha, Guda, Saindhava can be use.
MADANAPHALA CŪRṆA YOGAS
आतपशुष्कं वा चूर्णीकृतं जीमूतकादिकषायेण पित्ते कफस्थानगते पाययेदिति समानं पूर्वेण||
(Cha. Ka.1/20)
The dried seeds of Madanaphala under sunlight is processed with the decoction of Jīmūthaka, Ikṣvāku, Dhāmārgava, Kutaja and Krtavedana are made into powder and can administer in the cases of Kapahasthānagata Pitta.
MADANAPHALA VARTI AND LEHA YOGAS
फलपिप्पलीचूर्णानि पूर्ववत् फलादीनां षण्णामन्यतमकषायस्रुतानि वर्तिक्रियाः फलादिकषायोपसर्जनाःपेया इति समानं पूर्वेण| (Cha. Ka.1/21)
For the preparation of Madanaphala Varti Yoga the seeds of Madanaphala is boiled in the any of the decoction of Madanaphala, Jīmūthaka, Ikṣvāku, Dhāmārgava, Kutaja and Krtavedana then made into Varti.
फलपिप्पलीनामारग्वध –वृक्षक–स्वादुकण्टक–पाठा–पाटला–शार्ङ्गेष्टा–मूर्वा–सप्तपर्ण–नक्तमाल–पिचुमर्द–पटोल–सुषवी–गुडूची–सोमवल्क–द्वीपिकानां पिप्पली–पिप्पलीमूल–हस्तिपिप्पली–चित्रक–शृङ्गवेराणां चान्यतमकषायेण सिद्धो लेह इति समानं पूर्वेण|| (Cha. Ka.1/22)
For Vamana seeds of Madanaphala is made into Lehya by boiling with the decoction of anyone of Āragvadha, Kutaja, Svādhukandaka, Pātha, Pātala, Gunja, Mūrvā, Saptaparna, Naktamāla, Pichumarda, Patola, Susavi, Guduci, Somavalka, Dvipika, Pippali, Pippali Mūla, Hastipippali, Citraka, Śṛṅgavera.
MADANAPHALA UTKĀRIKĀADI YOGAS
Madanaphala Utkārikā and Modhaka Yoga:
फलपिप्पलीष्वेला–हरेणुका–शतपुष्पा–कुस्तुम्बुरु–तगर–कुष्ठ–त्वक्–चोरक–
मरुबकागुरु–गुग्गुल्वेलवालुक–श्रीवेष्टक–परिपेलव–मांसी–शैलेयक–स्थौणेयक–सरल–
पारावतपद्यशोकरोहिणीनां विंशतेरन्यतमस्य कषायेण साधितोत्कारिका उत्कारिकाकल्पेन, मोदका वा मोदककल्पेन, यथादोषरोगभक्ति प्रयोज्या इति समानं पूर्वेण|| (Cha. Ka.1/25)
The seeds of Madanaphala is cooked with any one of the decoctions of Ela, Hareṇuka, Śatapuṣpa, Kustumburu, Tagara, Kuṣṭa, Tvak, Coraka, Marūbaka, Agaru, Guggulu, Ela Valūka, Śriveshtaka, Paripelava, Māṃsi, Śaileyaka, Sthauneyaka, Sarala, Paravātapadi and Asoka-rohini. With the paste (Kalka) thus obtained, Utkārikā (Pancake) or Modaka can be prepared.
Madanaphala Yoga as Śaṣkulī and Pūpa:
(1) फलपिप्पलीस्वरसकषायपरिभावितानि तिलशालितण्डुलपिष्टानि
तत्कषायोपसर्जनानि शष्कुलीकल्पेन वा शष्कुल्यः, पूपकल्पेन वा पूपाः इति समानं पूर्वेण|| (Cha. Ka.1/24)
(2) एतेनैव च कल्पेन सुमुख–सुरस–कुठेरक–काण्डीर–कालमालक–पर्णासक–
क्षवक–फणिज्झक–गृञ्जन–कासमर्द–भृङ्गराजानां पोटेक्षुवालिका–कालङ्कतक दण्डैरकाणां चान्यतमस्य कषायेण कारयेत्||
(Cha. Ka.1/25)
The paste(Kalka) of tila and śali rice should be prepared by the decoction or the Svarasa of Madanaphala. And again, this paste(Kalka) is processed with the decoction of Madanaphala. Out of this Śaṣkulī / Pūpa is prepared. Any of the decoction of Sumuka, Surasa, Kuteraka, Kandira, Kalamāla, Parnaśaka, Kśavaka, Phāninjjaka, Grinjana, Kāsamardha, Bhṛṅgarāja, Pota, Iksuvālika, Kālankataka, and Dandairaka can also be used according to the condition. Using this paste also Śaṣkulī / Pūpa can be prepared for inducing Vamana.
Madanaphala Yoga as Badara Ṣāḍavadi:
तथा बदरषाडव–राग–लेह–मोदकोत्कारिका–तर्पण–पानक–मांसरस–यूष–मद्यानां मदनफलान्यन्यतमेनोपसृज्य यथादोषरोगभक्ति दद्यात्; तैः साधु वमतीति|| (Cha. Ka.1/26)
For Vamana after accessing the Avasthā of Dośa, Rogi and Sātmyata, the seeds of Madanaphala may be added to any one of the preparations like Badara Ṣāḍava, Rāga, Leha, Modaka, Utkārikā, Tarpana, Pānaka, Māṃsarasa, Yuśa, and Madya can administer.
INTRODUCTION
षट् क्षीरे मदिरामण्डे एको द्वादश चापरे|
सप्त चारग्वधादीनां कषायेऽष्टौ च वर्तिषु||
जीवकादिषु चत्वारो घृतं चैकं प्रकीर्तितम्|
कल्पे जीमूतकानां च योगास्त्रिंशन्नवाधिकाः (Cha. Ka.1/14)
In Jīmūtaka Kalpa 39 pharmaceutics recipes has been explained in detail. Six preparation in Kṣīra, one in the Surāmaṇḍa (supernatant part of wine), twelve recipes prepared by boiling with decoctions of Guduci etc., seven in the decoction of the Āragvadha etc., eight recipes in the form of pills, four preparation in the juice of Jivaka etc. and one recipe of ghee were explained detail in this Adhyāya.
SYNONYMS AND THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS OF JĪMŪTAKA
कल्पं जीमूतकस्येमं फलपुष्पाश्रयं शुणु|
गरागरी च वेणी च तथा स्याद्देवताडकः||
जीमूतकं त्रिदोषघ्नं यथास्वौषधकल्पितम्|
प्रयोक्तव्यं ज्वरश्वासहिक्काद्येष्वामयेषु च|| (Cha. Ka.1/3-4)
The synonyms of Jīmūtaka are Garāgari, Veni and Devatādaka. The flowers and fruits of Jīmūtaka are having therapeutic use. Jīmūtaka is Tridośaghnam and it is also indicated in fever, asthma and Hikka.
JĪMŪTAKA KṢĪRA YOGA
यथोक्तगुणयुक्तानां देशजानां यथाविधि|
पयः पुष्पेऽस्य, निर्वृत्ते फले पेया पयस्कृता||
लोमशे क्षीरसन्तानं, दध्युत्तरमलोमशे|
शृते पयसि दध्यम्लं जातं हरितपाण्डुके||
जीर्णानां च सुशुष्काणां न्यस्तानां भाजने शुचौ|
चूर्णस्य पयसा शुक्तिं वातपित्तार्दितः पिबेत्|| (Cha. Ka.1/5-7)
Jīmūtaka Puṣpa Siddha Kṣīra, Kṣīra Peya prepared with the Jīmūta Phala; Kṣīra Santhāna prepared out of Jīmūtaka Phala; Dadhi prepared out of Jīmūta Phala; Dadhyamla (Sour Dadhi) out of matured fruits of Jīmūta; Cūrṇa of dried fruits of Jīmūta in one Śukti Pramāṇa along with milk is indicated for the patients who are afflicted with Doṣas like Vāta and pitta .
JĪMŪTAKA SURAMAṆḌA YOGA
आसुत्य च सुरामण्डे मृदित्वा प्रस्रुतं पिबेत्|
कफजेऽरोचके कासे पाण्डुरोगे सयक्ष्मणि|| (Cha. Ka.1/8)
For the preparation of Sura – Maṇḍa Jīmūtaka Yoga, the Cūrṇa of Jīmūtaka Phala is soaked in the Suramaṇḍa and kept overnight. Thereafter net day it is stirred and strained. The Suramaṇḍa preparation thus obtained can be used in Kaphaja Arocaka, Kāsa and Pāndu Roga (anemia)and Rājayakṣma.
JĪMŪTAKA KAṢĀYA YOGAS
द्वे चापोथ्याथवा त्रीणि गुडूच्या मधुकस्य वा|
कोविदारादिकानां वा निम्बस्य कुटजस्य वा||
कषायेष्वासुतं पूत्वा तेनैव विधिना पिबेत्| (Cha. Ka.1/9)
The Jīmūtaka Phala (2-3)is boiled with the any of the decoctions of Guduci, Yaṣtīmadhu, Kovidāra, Karbudāra, Nīpa, Vidula, Bimbī, Śaṇapuṣpī, Sadā Puṣpī, Prathyak Puṣpī, Nimba and Kutaja. Then the liquid should be fermented, filtered and given to the patient for inducing therapeutic emesis.
JĪMŪTAKA MĀTRĀ YOGA
मात्राः स्युः फलवच्चाष्टौ कोलमात्रास्तु ता मताः|| (Cha. Ka.1/11)
Using Kovidārādi decoctions, the Jīmūtaka pills should be prepared for Vamana. 2 parts of the seeds of Jīmūtaka is added with 6 parts of decoctions of any one of Kovidāra, Karbudāra, Nīpa, Vidula, Bimbī, Śaṇapuṣpī, Sadāpuṣpī, or Prathyakpuṣpī, and it then strained for 21 times. With this liquid the seeds are undergone Bhāvana and pills are prepared. Pill size can be equal to the size of Āmalaka, Vibhītaki or Harītaki. One or two pills along with the any of Kovidārādi Kaṣāya (above mentioned) can be administered.
JĪMŪTAKA CŪRṆA WITH ĀRAGVADHĀDI KAYAŚA
अथवाऽऽरग्वधादीनां सप्तानां पूर्ववत् पिबेत्||
एकैकस्य [२] कषायेण पित्तश्लेष्मज्वरार्दितः| (Cha. Ka.1/10)
In the conditions Like Kapha – Pitta Jvara the Cūrṇa of Jīmūtaka along with the decoctions like Āragvadha, Vrkśaka, Svādhu Kandaka, Pātha, Patola , Śṛṅgaveshta, Mūrvā is indicated.
JĪMŪTAKA CŪRṆA WITH JIVAKĀDI SVARASA
जीवकर्षभकेक्षूणां शतावर्या रसेन वा|
पित्तश्लेष्मज्वरे दद्याद्वातपित्तज्वरेऽथवा|| (Cha. Ka.1/12)
In the conditions like Pittam Kapahaja Jvara or in Vāta Pittika Jvara the Cūrṇa of Jīmūtaka along with the Svarasa of Jīvaka, Rśabhaka, Ikṣu, Śatavari is indicated.
JĪMŪTAKA GHṚTA YOGA
तथा जीमूतकक्षीरात् समुत्पन्नं पचेद्घृतम्|
फलादीनां कषायेण श्रेष्ठं तद्वमनं मतम्|| (Cha. Ka.1/13)
For Vamana, primarily the Ghṛta is prepared with Jīmūtaka Siddha Kṣīra and later again this Ghṛta is processed with any of the decoction of Madanaphalādi Vāmaka Dravya is used. It is considered as an excellent recipe for emesis.
INTRODUCTION
पयस्यष्टौ सुरामण्ड–मस्तु–तक्रेषु च त्रयः|
घ्रेयं सपललं तैलं वर्धमानाः फलेषु षट्||
घृतमेकं कषायेषु नवान्ये मधुकादिषु|
अष्टौ वर्तिक्रिया लेहाः पञ्च मन्थो रसस्तथा||
योगा इक्ष्वाकुकल्पे ते चत्वारिंशच्च पञ्च च|
उक्ता महर्षिणा सम्यक् प्रजानां हितकाम्यया|| (Cha. Ka. 3/21)
In Ikṣvāku Kalpa 45 pharmaceutics recipes of Ikṣvāku has been explained in detail. Eight milk preparations, three preparations consisting of one in supernatant part of wine, one in whey and one in butter milk, one Ghṛeya Yoga, one preparation with Tila paste, one oil preparation and six preparation of successively increasing dose of seeds with Madanaphala, one ghee preparation, nine with decoctions of Madhukādi Vamanopaga drugs, eight pills, five linctuses, one of demulcent drink and one of meat-juice were explained detail in this Adhyāya by the grate sage, desirous of the welfare of humanity.
SYNONYMS AND THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS OF IKṢVĀKU
लम्बाऽथ कटुकालाबूस्तुम्बी पिण्डफला तथा||
इक्ष्वाकुः फलिनी चैव प्रोच्यते तस्य कल्पना|
कासश्वासविषच्छर्दिज्वरार्ते कफकर्षिते||
प्रताम्यति नरे चैव वमनार्थं तदिष्यते| (Cha. Ka.3/3)
Lamba, Katukālābu, Tumbi, Pinda – Phala, and Phalini are the synonyms of Ikṣvāku.
Kāsa, Śvāsa, Viṣa, Chardhi, Jvara, Kapha Karṣita (dried) Avasthā, and for those who are distressed with palpitation are indicated for administering Ikṣvāku Yogas.
IKṢVĀKU KṢĪRA YOGAS
अपुष्पस्य प्रवालानां मुष्टिं प्रादेशसम्मितम्||
क्षीरप्रस्थे शृतं दद्यात् पित्तोद्रिक्ते कफज्वरे|
पुष्पादिषु च चत्वारः क्षीरे जीमूतके यथा|| (Cha. Ka.3/5)
One Prastha of Kṣīra which is processed with one Muṣṭi Pramāṇa (fistful) of Ikṣvāku sprouts can be given to the patients who all are suffering from Kaphaja Jvara associated with Pitta. Kṣīra processed with Puṣpa of Ikshvagu; Kṣīra Peya prepared with Phala of Ikṣvāku; Kṣīra Santhāna with Ikṣvāku Phala and Dadhi prepared from milk processed with Phala of Ikṣvāku.
योगा हरितपाण्डूनां सुरामण्डेन पञ्चमः| (Cha .Ka. 3/6)
The matured fruits of Ikṣvāku (Phala with green and yellowish colour) is soaked in Surāmaṇḍa and kept overnight. Thereafter it is stirred and strained.
फलस्वरसभागं च त्रिगुणक्षीरसाधितम्||
उरःस्थिते कफे दद्यात् स्वरभेदे च पीनसे| (Cha. Ka. 3/7)
Ikṣvāku Svarasa (one part), processed in Kṣīra (3 parts), Jala (4 parts) can be administered to the patients who all are suffering from Kapha vitiation in chest, Svarabheda (hoarseness of voice), Pīnasa (coryza).
जीर्णे मध्योद्धृते क्षीरं प्रक्षिपेत्तद्यदा दधि||
जातं स्यात् सकफे कासे श्वासे वम्यां च तत् पिबेत्| (Cha. Ka. 3/8)
Ikṣvāku Siddha Dadhi is indicated in Kaphaja Kāsa, Śvāsa and Chardhi.
अजाक्षीरेण बीजानि भावयेत् पाययेत् च||
विषगुल्मोदरग्रन्थिगण्डेषु श्लीपदेषु च| (Cha. Ka. 3/9)
In Rogas like Gulma, Udara, Viṣa, Grandhi (nodules), Gaṇḍa (enlargement of thyroid gland), Slīpada (elephantiasis), Aja Kṣīra processed (Bhāvana) with the Ikṣvāku Bīja is indicated.
IKṢVĀKU MASTU AND TAKRA YOGA
मस्तुना वा फलान्मध्यं पाण्डुकुष्ठविषार्दितः||
तेन तक्रं विपक्वं वा सक्षौद्रलवणं पिबेत्| (Cha. Ka. 3/10)
In cases of anaemia, Kuṣṭa and Viṣa the Ikṣvāku Phalamajja Siddha Masthu is indicated.
For therapeutic emesis the Ikṣvāku Phalamajja along with Takra, Madhu and salt can be given.
IKṢVĀKU GHṚEYA YOGAM
तुम्ब्या फलरसैः शुष्कैः सपुष्पैरवचूर्णितम्||
छर्दयेन्माल्यमाघ्राय गन्धसम्पत्सुखोचितः| (Cha. Ka. 3/11)
For Ghṛeya Yoga the fruit juice and the Cūrṇa of dried flowers are sprinkled over the flower garland and administered for Vamana.
IKṢVĀKU MĀTRĀ
कषायैः कोविदाराद्यैर्मात्राश्चफलवत् स्मृताः|| (Cha. Ka. 3/11)
Using Kovidārādi decoctions, the Ikṣvāku pills should be prepared for Vamana. 2 parts of the seeds of Ikṣvāku added with 6 parts of decoctions of any one of Kovidāra, Karbudāra, Nīpa, Vidula, Bimbī, Śaṇapuṣpī, Sadā Puṣpī, or Prathyak Puṣpī, and it then strained for 21 times. With this liquid the seeds are undergone Bhāvana and pills are prepared. Pill size can be equal to the size of Āmalaka, Vibhītaki or Harītaki. One or two pills along with the any of Kovidārādi Kaṣāya (above mentioned) can be administered.
यष्ट्याह्वकोविदाराद्यैर्मुष्टिमन्तर्नखं पिबेत्|| (Cha. Ka. 3/14)
The seeds of Ikṣvāku in a Mātrā of Antarnakha Muṣṭi Pramāṇa (one closed fistful of seeds) can be taken along with any of the decoction of Yashtimadhu, Kovidāra, Karbudāra, Nīpa, Vidula, Bimbī, Śaṇapuṣpī, Sadā Puṣpī, or Prathyak Puṣpī, for the therapeutic emesis.
भक्षयेत् फलमध्यं वा गुडेन पललेन च||
इक्ष्वाकुफलतैलं वा सिद्धं वा पूर्ववद्घृतम्| (Cha. Ka. 3/13)
For emesis the Ikṣvāku Phala Majja (fruit pulp) can be administered along with either Guda or Palala. The Ikṣvāku Phala Siddha Taila or Ghṛta can also induce emesis.
IKṢVĀKU LEHYA YOGAS
बिल्वमूलकषायेण तुम्बीबीजाञ्जलिं पचेत्||
पूतस्यास्य त्रयो भागाश्चतुर्थः फाणितस्य तु|
सघृतो बीजभागश्च पिष्टानर्धांशिकांस्तथा ||
महाजालिनिजीमूतकृतवेधनवत्सकान्|
तं लेहं साधयेद्दर्व्या घट्टयन्मृदुनाऽग्निना||
यावत् स्यात्तन्तुमत्तोये पतितं तु न शीर्यते|
तं लिहन्मात्रया लेहं प्रमथ्यां च पिबेदनु||
कल्प एषोऽग्निमन्थादौ चतुष्के पृथगुच्यते| (Cha. Ka. 3/15-18)
For the preparation of the Lehya, one Añjali Pramāṇa seeds of Ikṣvāku is boiled in the decoction of Bilva (8 Añjali) and reduced to one fourth. To three parts of this strained decoction one part of Phāṇita and one part of Ghṛta should be added. To this half parts each of the paste of Maha Jalini, Ikṣvāku, Krtavedana, Vatsaka should be added. Instead of the Bilva Kaṣāya based on the Roga Rogi Avasthā one can select the decoction of Agnimantha Mūlam, Shyonāka, Pātala, Gambhāri. The linctus should be prepared by cooking over mild fire by continuous stirring. After the intake of Lehya Pramathya can be used as post prandial drink.
IKṢVĀKU MANTHA PREPARATION
शक्तुभिर्वा पिबेन्मन्थं तुम्बीस्वरसभावितैः||
कफजेऽथ ज्वरे कासे कण्ठरोगेष्वरोचके| (Cha. Ka. 3/19)
In Kaphaja Jvara, Kāsa, kaṇṭha Roga, Arocaka the Mantha prepared with the Ikṣvāku Svarsa Bhāvita Saktu ( the roasted barley flour) is indicated.
IKṢVĀKU MĀṂSARASA PRAYOGA
गुल्मे मेहे प्रसेके च कल्कं मांसरसैः पिबेत्|
नरः साधु वमत्येवं न च दौर्बल्यमश्नुते|| (Cha. Ka. 3/20)
In Gulma, Meha and Praseka the paste of Iksvaku Bīja along with the Māṃsarasa can administer to induce emesis. Such therapeutic emesis will not cause any debility in Gulmādi patients.
Dhāmārgava is an ayurvedic drug which is known for is Vāmaka (emetic) property. It is included as one among the Phalini Dravyas and inspite of its Vāmaka action, the drug is also used as one of the Asthāpana Basti Dravya.
Latin Name: – Luffa cylindrica (Linn.) M.J.Roem.
Family: – Cucurbitaceae
Synonyms: – Luffa aegyptiaca Mill., Luffa pentandra Roxb.
English Name: – Sponge gourd, Smooth luffa.
Botanical Description: – The plant is a climber which is having stout stems. The angles of the stem are 5 angled, twisted, glabrous. Contains tendrils which are usually 3 fids. The leaves are about orbicular in shape with about 10 – 20 cm in length.
SYNONYMS OF DHĀMĀRGAVA KALPA
कर्कोटकी कोठफला महाजालिनिरेव च|
धामार्गवस्य पर्याया राजकोशातकी तथा || (Cha. Ka. 4/3)
कर्कोटकी – Karkoṭakī
कोठफला – Koṭapāla
महाजालिनि – Mahājālīni
राजकोशातकी – Rajakośataki
INDICATIONS OF DHĀMĀRGAVA
गरे गुल्मोदरे कासे वाते श्लेष्माशयस्थिते|
कफे च कण्ठवक्रस्थे कफसञ्चयजेषु च||
रोगेष्वेषु प्रयोज्यं स्यात् स्थिराश्च गुरवश्च ये | (Cha. Ka. 4/4-5)
Dhāmārgava should be used in conditions of Gara, Gulma, Udara, Kāsa, Vāta in Kapha Stāna, Kapha in throat (Kaṇḍa) and Vakra (mouth), diseases caused due to Kapha Sañcaya.
TOTAL PREPARATIONS OF DHĀMĀRGAVA KALPA
पल्लवे नव चत्वारः क्षीर एकः सुरासवे |
कषाये विंशतिः कल्के दश द्वौ च शकृद्रसे ||
अन्न एकस्तथा घ्रेये दश लेहास्तथा घृतम् |
कल्पे धामार्गवस्योक्ताः षष्टिर्योगा महर्षिणा || (Cha. Ka. 4/19-20)
Total Preparations from this Kalpa: – 60 formulations
Sl. No | Preparation Type | Number of Preparations |
1. | Using पल्लव (tender leaves) | 9 |
2. | क्षीर (Milk) Preparation | 4 |
3. | सुरासव (Alcohol) Preparation | 1 |
4. | कषाय (Kaṣāya) Preparation | 20 |
5. | कल्क (Kalka) Preparation | 1 |
6. | शकृद्रस Preparation | 12 |
7. | अन्न – Along with Food | 1 |
8. | घ्रेय – for Inhalation | 1 |
9. | लेह (Linctus) Preparation | 10 |
10. | घृत (Ghee) Preparation | 1 |
FORMULATION USING PALLAVA (TENDER LEAVES)
प्रवालस्वरसं शुष्कं कृत्वा च गुलिकाः पृथक् |
कोविदारादिभिः पेयाः कषायैर्मधुकस्य च || (Cha. Ka. 4/6)
The tender leaves are dried and it is made to pills which is administered along with the Kaṣāya prepared out of any one of the 8 drugs from Kovidārādi Gana / Madhūka.
ghṛeya prayoga – for inhalation
चूर्णैर्वाऽप्युत्पलादीनि भावितानि प्रभूतशः |
रसक्षीरयवाग्वादितृप्तो घ्रात्वा वमेत् सुखम् || (Cha. Ka. 4/10)
Patient who has consumed Māṃsarasa, milk, Yavāgu will easily vomit by inhaling the Cūrṇa which was impregnated over Utpalādinām. Here by उत्पलादीना, Ācārya means flower of Sugandika or Padmaka.
LEHA (LINCTUS) PREPARATION
जीवकर्षभकौ वीरामात्मगुप्तां शतावरीम् |
काकोलीं श्रावणीं मेदां महामेदां मधूलिकाम् ||
एकैकशोऽभिसञ्चूर्ण्य सह धामार्गवेण ते |
शर्करामधुसंयुक्ता लेहा हृद्दाहकासिनाम् ||
सुखोदकानुपानाः स्युः पित्तोष्मसहिते कफे (Cha.Ka. 4/13-14)
Here the drugs from Jivaka till Madhūlika are powdered separately and then mixed with Dhāmārgava. This is mixed with Madhu and Śarkara and consumed as Lehya in case of Hṛdroga and Kāsa. If the patient is suffering from Kaphapitta Saṃsarga Vyādhi, then the above should be consumed with luke warm water.
Dhāmārgava as Vāmaka Dravya for Mānasika Vyādhi
जात्याः सौमनसायिन्या रजन्याश्चोरकस्य च |
वृश्चीरस्य महाक्षुद्रसहाहैमवतस्य च ||
बिम्ब्याः पुनर्नवाया वा कासमर्दस्य वा पृथक् |
एकं धामार्गवं द्वे वा कषाये परिमृद्य तु ||
पूतं मनोविकारेषु पिबेद्वमनमुत्तमम् | (Cha. Ka. 4/16-18)
One or Two fruits of Dhāmārgava are powdered and then added to the Kaṣāya prepared out of any of the drug from Jāti till Kāsamarda. They should be filtered and then taken as an excellent Vāmaka Dravya.
Vatsaka is also another emetic drug explained by Caraka under Kalpa Sthāna. The fruits and seeds of Vatsaka are used entirely for the purpose of Vamana. This drug is also known by the name Sveta Kuṭaja or Punkuṭaja.
Latin Name: – Holarrhena antidysentrica Linn.Wall
Family: – Apocynaceae
English Name: – Kurci
Botanical Description: – Vatsaka is a small tree or shrub like plant with pale bark. Leaves are broadly ovate to elliptic, obtuse or obtusely acuminate, glabrous or more or less pubescent. The plant is distributed throughout India, especially in the wet forests and tropical Himalayas, up to an altitude of 1200m.
Classical Description: – in Caraka Samhita the use of Vatsaka can be seen in Caraka Sutrasthāna 3rd chapter, where Ācārya explains that the leaves of Vatsaka are used to treat Kuṣṭa, Kilasa, Indraluota, Arśa etc. The fruit of Vatsaka are used as Stanya Śhodhana Mahākaṣāya and Asthāpanopaga Dravya.
SYNONYMS OF VATSAKA
वत्सकः कुटजः शक्रो वृक्षको गिरिमल्लिका |
बीजानीन्द्रयवास्तस्य तथोच्यन्ते कलिङ्गकाः || (Cha. Ka. 5/4)
The drug is known by the names Vatsaka, Kuṭaja, Śakra, Vṛkṣaka and Girimallika. The Bīja /seeds is known by the name Indrayava and Kaliṅgaka.
TYPES & DESCRIPTION
अथ वत्सकनामानि भेदं स्त्रीपुंसयोस्तथा |
कल्पं चास्य प्रवक्ष्यामि विस्तरेण यथातथम् || (Cha. Ka. 5/3)
बृहत्फलः श्वेतपुष्पः स्निग्धपत्रः पुमान् भवेत् |
श्यामा चारुणपुष्पा स्त्री फलवृन्तैस्तथाऽणुभिः || (Cha. Ka. 5/5)
There are 2 types of Vatsaka. Male variety and Female variety. The male plant has big fruits, white flowers and smooth leaves whereas the female plant is blackish with reddish flowers and smaller fruits.
BENEFITS OF VATSAKA
रक्तपित्तकफघ्नस्तु सुकुमारेष्वनत्ययः |
हृद्रोगज्वरवातासृग्वीसर्पादिषु शस्यते || (Cha. Ka. 5/6)
Vatsaka is beneficial against Raktapitta and Kaphaja Rogas. It can be used as Vāmaka Dravya for even Sukumāra persons. It is indicated in cardiac disorders, fever, Vātarakta, erysipelas etc.
FORMULATIONS FROM VATSAKA KALPA
Total formulation of this Kalpa: – 18 formulations
कषायैर्नव चूर्णैश्च पञ्चोक्ताः सलिलैस्त्रयः|
एकश्च कृशरायां स्याद्योगास्तेऽष्टादश स्मृताः || (Cha. Ka. 5/12)
Sl. No | Preparation Type | Number of Preparations |
1. | कषाय (Kaṣāya) Preparation | 9 |
2. | चूर्ण (Powder) Preparation | 5 |
3. | सलिल Along with water | 3 |
4. | कृशर Preparation | 1 |
IMPORTANT FORMULATIONS
काले फलानि सङ्गृह्या तयोः शुष्काणि निक्षिपेत् |
तेषामन्तर्नखं मुष्टिं जर्जरीकृत्य भावयेत् ||
मधुकस्य कषायेण कोविदारादिभिस्तथा |
निशि स्थितं विमृद्यैतल्लवणक्षौद्रसंयुतम् ||
पिबेत्तद्वमनं श्रेष्ठं पित्तश्लेष्मनिबर्हणम् | (Cha. Ka. 5/7-9)
The fruit of both types of Vatsaka when ripened and dry should be collected at proper time. It should be crushed using our hands then it should be impregnated with the decoction of Madhūka and Kovidārādi drugs and kept for the whole night. On the next morning it should be pressed and added with salt and honey and used as an excellent Vāmaka Dravya against Pitta and Kapha.
अष्टाहं पयसाऽऽर्केण तेषां चूर्णानि भावयेत्||९||
जीवकस्य कषायेण ततः पाणितलं पिबेत्|
फलजीमूतकेक्ष्वाकुजीवन्तीनां पृथक् तथा||१०||
सर्षपाणां मधूकानां लवणस्याथवाऽम्बुना
कृशरेणाथवा युक्तं विदध्याद्वमनं भिषक्||११|| (Cha. Ka. 5/9-11)
The Bīja Cūrṇa should be impregnated with latex of Arka for eight days and then should be taken in quantity of 10 gms with decoction of Jīvaka. Likewise this may be taken with decoction of Madanaphala, Jīmūtaka, Ilśavaku and Jivanti separately. The powder may be taken with water of mustard, Madhūka or salt or the physician may administer it as emetic mixed with Kriśara.
Kṛtavedhana (Luffa acutangular Linn. Roxb) is used as a strong and powerful emetic drug. It is very pungent, sharp and hot so used in deep seated diseases for e.g Gulma, Kuṣṭa, Gara Viṣa, etc. it is included as one among the Phalini Dravya. And also among the Tikta Skanda.
Latin Name: Luffa acutangular Linn. Roxb
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Sanskrit Synonym: Rājīmatphala, Jālini, Mṛdaṅgaphala
English Name: Ribbed luffa, ridged gourd
Botanical Description: -the leaves and flowers of the plant are smaller. The leaves at first are white in colour. The fruits are obovoid, obtusely conical at both ends, 5 to 10 cm long. The plant is slightly pungent, acrid, bitter, laxative, carminative digestible a tonic to the intestines.
RASA PAÑCAKA
RASA: Tikta
GUNA: Laghu, Rukśa, Tīkṣṇa
VĪRYA: Uṣṇa
VIPĀKA: Katu
PRABHĀVA: Ubhayatobhāgahara
SYNONYMS
कृतवेधननामानि कल्पं चास्य निबोधत |
क्ष्वेडः कोशातकी चोक्तं मृदङ्गफलमेव च || (Cha. Ka. 6/3)
The major known synonyms of Kṛtavedhana are Kṣveḍā, Kośataki and Mṛdaṅgaphala.
QUALITIES
अत्यर्थकटुतीक्ष्णोष्णं गाढेष्विष्टं गदेषु च |
कुष्ठपाण्ड्वामयप्लीहशोफगुल्मगरादिषु || (Cha. Ka. 6/4)
Kṛtavedhana is intensely pungent in taste and is having an Uṣṇa potency. Very much effective in treating deep seated diseases like Kuṣṭa, Pāndu, Plihāvrddhi, Śotha, Gulma, etc.
FORMULATIONS FROM THIS KALPA
Total formulations in this Kalpa – 60 Formulations
क्षीरे द्वौ द्वौ सुरा चैका क्वाथा द्वाविंशतिस्तथा|
दश पिच्छा घृतं चैकं षट् च वर्तिक्रियाः शुभाः||१३||
लेहेऽष्टौ सप्त मांसे च योग इक्षुरसेऽपरः|
कृतवेधनकल्पेऽस्मिन् षष्टिर्योगाः प्रकीर्तिताः||१४|| (Cha. Ka. 6/13-14)
Sl. No | Preparation Type | No of Preparation |
1. | Milk | 4 |
2. | Alcohol beverage | 1 |
3. | Kvātha | 20 |
4 | Picchā | 10 |
5. | Ghee | 1 |
6. | Varti | 6 |
7. | Leha | 8 |
8. | Māṃsa | 7 |
9. | Ikṣu Rasa | 1 |
IMPORTANT FORMULATIONS
कषायेषु फलादीनामानूपं पिशितं पृथक् |
कोशातक्या समं पक्त्वा रसं सलवणं पिबेत् || (Cha. Ka. 6/11)
In the Kaṣāya prepared using Phalini drugs separately, meat of Anūpadeśa animals should be cooked along with Kośataki and then should be taken.
फलादिपिप्पलीतुल्यं तद्वत् क्ष्वेडरसं पिबेत् | (Cha. Ka. 6/12)
As said above meat soup prepared with Kośataki and added with seeds of Phalini drugs are used.
क्ष्वेडं कासी पिबेत् सिद्धं मिश्रमिक्षुरसेन च || (Cha. Ka. 6/12)
If a patients is suffering from cough, he / she should take Kośataki mixed and cooked with sugarcane.
IMPORTANT SLOKA
फलजीमूतकेक्ष्वाकुकल्पो धामार्गवस्य च||
पञ्चमो वत्सकस्योक्तः षष्ठश्च कृतवेधने| (Ch.Su.30/62)
According to Ācārya Caraka, Vamana Drugs Are Madanaphala (Randia Dumetorum), Jīmūta (Luffa Echinata), Ikṣvāku (Lagenaria Vulgaris), Dhāmārgava (Luffa Cylindrica), Vatsaka (Holarrehena Antidysentrica), Kṛtavedana (Luffa Acutangula)
मदनमधुकलम्बानिम्बबिम्बीविशाला-
त्रपुसकुटजमूर्वादेवदालीकृमिघ्नम्|
विदुलदहनचित्राः कोशवत्यौ करञ्जः
कणलवणवचैलासर्षपाश्र्छर्दनानि|| (AH.Su.15/1)
The drugs mentioned in Vamana Dravya Gaṇa explained by Ācārya Vāgbhaṭa are Madanaphala (Randia dumetorum), Madhuka (Glycyrrhiza glabra), Lamba (Lagenaria siceraria), Nimba (Azadirachta indica), Bimbi (Coccinia indica), Viśāla (Citrullus colocynthis), Trapusa (Cucumis sativus), Kutaja (Holarrhina antidysenterica), Mūrva (Marsdenia tenacissima), Devatāli (Luffa echinata), Krmighna (Embelia ribes), Vidula (Barringtonia acutangula), Dahana (Plumbago zeylanica), Citra (Trichosanthes anguina), 2 types of Kośavati – Kośātaki (Luffa acutangula) and Dhāmārgava (Luffa cylindrica), Karañja (Pongamia pinnata), Kaṇa (Piper longum), Lavaṇa (salt), Vacā (Acorus calamus), Ela (Elettaria cardamomum), Sarśapa (Brassica campestris).
मधुमधुककोविदारकर्बुदारनीपविदुलबिम्बीशणपुष्पीसदापुष्पाप्रत्यक्पुष्पा इति दशेमानि वमनोपगानि भवन्ति || (Ch.Su.4/13)
The 10 Vamanopaga Dravyas mentioned by Ācārya Caraka are Madhu (honey), Madhuka (Glycyrrhiza glabra), Kovidāra (Bauhinia purpurea), Karbudāra (Bauhinia variegata), Nīpa (Anthocephalus cadamba), Vidula (Barringtonia acutangula), Bimbi (Coccinia indica), Śaṇapuṣpī (Crotalaria verrucose), Sadāpuṣpi (Calotropis gigantea), Pratyakpuṣpī (Achyranthes aspera).



