
PG Module 2
SNEHANA
EXPLANATORY NOTES
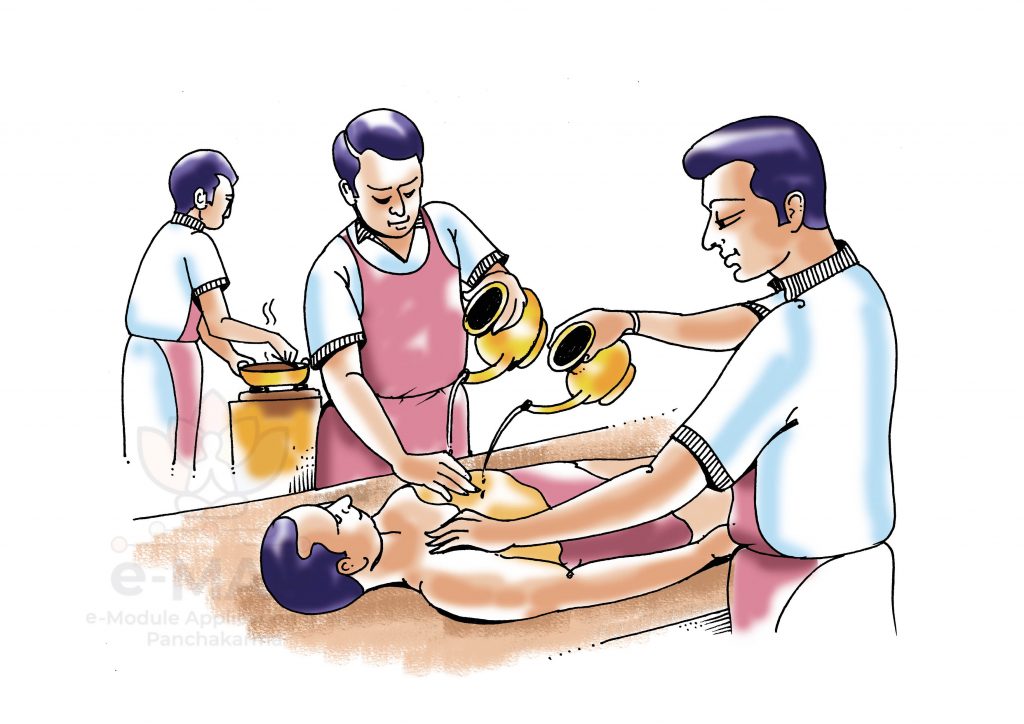
PARIṢEKA
Pariṣeka is a svedana procedure under the category of sāgni sveda. It is a procedure in which medicated liquid in the form of taila, ghṛta or decoction based on the disease condition is poured over the patient’s body from a specified height in a continuous stream for a specific period of time.
SYNONYMS
Seka
Dhāra
Secana
Prasecana
Pizhichil (keraliya cikitsā)
INDICATION OF SEKA
Aayāma
Śoṣavāta
Pakṣāghāta
Apabāhuka
Akshepaka
Jihva stambha
Hanugraha
Gṛdhrasī
Vishvāci
Vātarakta
Kampa
Sarvāṅga and ekāṅga vāta
Gulma
Hemiplegia
Quadriplegia
Paraplegia
Osteoarthritis
Fibromyalgia
Guillain barre syndrome
Spinal stenosis
IVDP
BENEFITS
Dṛḍhata of dhātu
Vṛṣya
Sthirata of agni,varṇa and ojus
Jara māndya
Cira jīva
Helps in asthi bhagna
Maintains equilibrium of doṣās ( DHĀRA KALPA)
PROCEDURE:
PŪRVAKARMA
Sambhāra Sangraha
- Abhyaṅga table – 1
- Vessels – 3
- Induction stove – 1
- Cotton cloth – Towel
- Medicated oil for abhyaṅga – 100ml
- Dravya for the seka – 5-6ltrs
- Mugs/kindi – 4
- Therapist – 4
Preparation of patient
- Check for yogya /ayogya of Svedana
- Aṣṭavidha and daśavidha parīkṣā has to be checked.
- Swastivachana and prayer has to be done.
- The patient is asked to lie down on the abhyaṅga table with minimal clothes with legs extended.
- Sarvāṅga abhyaṅga has to be done for about 10 mins.
- Application of talam – āmalaki prepared has to be applied over the patients crown and has to be bandaged.
Preparation of medicine
Based on the procedure materials change
For sneha seka – Taila, Ghṛta, Trivṛt sneha, Yamaka will be used
Kaṣāya seka – Daśamūla, Bala, Musta, Uśira, Chandana, Yaṣṭi, etc. dravyās will be used for making kaṣāya.
Takra dhāra – takra processed with required medicinal drugs is used.
PRADHĀNA KARMA
- The medicine used for the seka has to be heated by keeping it in a hot water bath.
- The seka over the portion of the body below the hip is attended by two therapists on either side and two upper limbs and trunk is attended by two therapists on either side.
- The heated oil has to be filled in two mugs / kindi and has to be given to the therapist standing on either side.
- The therapist should confirm the temperature of the liquid by pouring on his hand on the dorsum side before pouring on the patient’s body.
- The dravya has to be poured from a height of 12 aṅgula in a continuous flow in a synchronised manner over the upper and lower parts of the body.
- The flow of dravya should be maintained in steady flow with a maintained speed and gentle massage in downward direction can be done with the left hand.
- Based on the condition, the dravya should be made hot or cold.
- The procedure can be done in sitting,supine,left lateral,right lateral,supine and sitting.
- The procedure can be carried out for about 40 mins.
Quantity of dravya used
- For the taila seka 1.5 praṣṭa of dravya has to be used for each usage.
- The sneha used for the first day can be reused for three days and on 4th day fresh taila has to be taken and can be used till the 6th day ,and on the 7th day the oil used on 4th day and 6th day has to be mixed and used .
PAŚCĀT KARMA
- After the seka the patient has to made to lie down on the abhyaṅga table
- The body has to be wiped with a towel.
- The body should not be exposed to a cold environment immediately after the procedure.
- The talam has to be removed.
- Patients can be advised to take hot water bath.
- The patient is advised to avoid the parihāra viṣayas
PRECAUTIONS
- The temperature of the oil or dravya has to be checked before pouring on the patient’s body.
- The height of the pouring has to be maintained.
- The pouring has to be steady and continuous.
LEPA
- लिप्यते अनेन इति लेप| (Śabdakalpadruma)
- द्रव्यमार्द्रम् शिलापिष्टं शुष्कं वा सद्रव तनु।
देहे प्रलेपनार्थं तल्लेप इत्युच्चते बुधै:। (Dravyaguṇa Vijñāna)
The medicine which is in the form of paste used for external application is called Lepa.
The medicines that can be prepared with Ārdra Dravya (wet drugs) and also by Śuṣkadravya (dried drugs) by utilizing liquid media and used for external application.The drugs are made into a fine powder form before use on the body. It is mixed with a liquid medium or other medium indicated in each preparation and made into a soft paste. Water, cow’s urine, oil and ghee are some of the media used for mixing. Wet medicinal drugs are made into a Kalka form, if the drugs are dry in state, they are converted into Kalka by adding water and grinding. This Kalka is used as an external application and it is called as Lepa Kalpana. Pharmaceutically, Lepa Kalpana is only meant for external application purposes.
Synonyms
आलेपस्य च नामानि लिप्तो लेपः लेपनम्। (शा. उ. लेपाध्याय)
Ālepana
Lipta
Lepa
Lepana.
Anulepa.
Classification
Lepa is classified on different basis as follows:
Suśruta Saṃhitā :Describes 3 varieties of Lepa
- Pralepa 2. Pradeha 3. Ālepa
स त्रिविधः- प्रलेपः, प्रदेह, आलेपश्च । प्रलेपप्रदेहयोरन्तरं – तत्र प्रलेपः शीतस्तनुरविशोषी विशोषी वा; प्रदेहस्तूष्णः शीतो वा बहलोऽबहुरविशोषी च; मध्यमोऽत्रालेपः । तत्र, रक्तपित्तप्रसादकृदालेपः; प्रदेहो वातश्लेष्मप्रशमनः शोधनो रोपणः शोफवेदनापहश्च; तस्योपयोगः क्षताक्षतेषु; यस्तु क्षतेषूपयुज्यते स भूयः ‘कल्क’ इति सञ्ज्ञां लभते निरुद्धालेपनसञ्ज्ञः; तेनास्रावसन्निरोधो मृदुता पूतिमांसापकर्षणमनन्तर्दोषता व्रणशुद्धिश्च भवति ।
(सु. सू. १८/६)
Aṣṭāṅga Saṅgraha : Describes 10 varieties of Lepa
- Snaihika
- Nirvāpaṇa
- Prasādana
- Stambhana
- Vilayana
- Pācana
- Pīḍana
- Śodhana
- Śoṣana
- Savarṇīkaraṇa
Ācārya Suśruta has advised incorporating of Sneha Dravya in Lepa formulation according to Doṣa:
Doṣa | Quantity of Snehadravya |
Vātaja Vyādhi | 1/4th part |
Pittaja Vyādhi | 1/6th part |
Kaphaja Vyādhi | 1/8th part |
Different technique of Lepa application
(सु. सू. 18/4)
Application of Lepa should be done gently by rubbing in an upward or reverse direction to the hairs over the skin, to make the action of the application quick and effective. Because of this the application enters through the Romakūpa and further gets absorbed through Svedavāhī Srotas and Sirāmukha thereby giving the results.
Doṣāgna – cūrṇa mixed with āranāla
Viṣaghna – ghṛta mixed with uṣṇa jala
Varṇya – nimbu svarasa, kṣīra
Thickness of Lepa
On the basis of nature of Lepa
Pralepa – which is applied cold, thin and which dries quickly.
Pradeha – which is applied warm, thick and remains moist for a long time.
The thickness of the Pralepa and Pradeha application over the skin should be equal to the thickness of a buffalo’s skin.
Time of application
Pralepa should not be applied at night nor it should be allowed to stay on after it dries up, whereas Pradeha can be allowed to stay on (even after drying) in order to cause constriction or pressure over the part of the body.
The heat of the body comes out through the skin pores at nights normally if medicinal applications are done at nights the skin pores get blocked and obstruct the transfer of body heat. So external applications should not be done at night. But in the case of apakva śotha, gambhīra śotha and śotha arising from rakta and śleṣma, application can be made even during the night. Lepa are effective as long as they are moist and once they dry up they will harm the skin.
Indication (caraka )
- Kuṣṭa
- Sidhma
- Rājayakṣma
- Śotha
- Arśa
- Visarpa
- Vraṇa



