
PG Module 3
SVEDANA
EXPLANATORY NOTES
व्याधौशीतेशरीरेचमहान्स्वेदोमहाबले| दुर्बलेदुर्बलःस्वेदोमध्यमेमध्यमोहितः[i]|
(Cha. Su. 14/12)
Based on intensity of Sveda–RogaBalā and RogiBalā
- MṛduSveda– Indicated in Durbalā, MṛduVyādhi. eg: Pāṇitāpa
- MadhyamaSveda-Madhyamavyādhi,MadhyamaBala eg: CūrṇapiṇḍaSveda, Kāyaseka
- MahāSveda– In MahāBalā Persons, MahāVyādhieg: JentākaSveda
[i] Cha.Su.14/12
ĒKĀṄGA SVEDA
Svedana is done to a specific part only. It is indicated where the pain is indicated in a specific region
Eg: Jānudhāra
SARVANGASVEDA
Here Svedana is done on whole body part.
Eg: SarvangaDhāra, All Kizhis
- SAṄKARASVEDA
तत्रवस्त्रान्तरितैरवस्त्रान्तरितैर्वापिण्डैर्यथोक्तैरुपस्वेदनंसङ्करस्वेदइतिविद्यात्|| (Cha. Su. 14/41)
The process of thermal sudation by means of a bolus with or withoutwrappingclothisknownas SaṅkaraSveda or PiṇdaSveda.
तिलमाषकुलत्थाम्लघृततैलामिषौदनैः|
पायसैःकृशरैर्मांसैःपिण्डस्वेदंप्रयोजयेत्||||
गोखरोष्ट्रवराहाश्वशकृद्भिःसतुषैर्यवैः|
सिकतापांशुपाषाणकरीषायसपूटकैः||||
श्लैष्मिकान्स्वेदयेत्पूर्वैर्वातिकान्समुपाचरेत्|
द्रव्याण्येतानिशस्यन्तेयथास्वंप्रस्तरेष्वपि[i]| (Cha. Su. 14/25)
- This isis of two types- Rūkṣa andSnigdha. Sudation donewithboluses of sesamum, blackgram, horsegram, sourpreparations, ghee, oilcookedrice, ricecookedwithmilk, preparation of rice and pulse, meatiscalledas SnigdhaPiṇdaSveda. It isspecificallyindicated in VātaRōga.
- Sudation donewithfaeces of cow, ass, camel, pig and horse, huskedbarley, sand, dust, stone pieces, driedcowdung and ironballsiscalled as RūkṣaPiṇdaSveda. It isindicatedin KaphajaVikāra.
Indications :-
RūkṣaCūrṇaPiṇḍaSveda– KaphapradhānaRoga, ĀmajanyaRoga, MedoRoga, ĀmaVāta
SnigdhaCūrṇaPiṇḍaSveda–Vātapradhānaconditions, Sandhigatavāta, KaṭīŚūla
- PRASTARASVEDA
शूकशमीधान्यपुलाकानांवेशवारपायसकृशरोत्कारिकादीनांवाप्रस्तरेकौशेयाविकोत्तरप्रच्छदेपञ्चाङ्गुलोरुबूकार्कपत्रप्रच्छदेवास्वभ्यक्तसर्वगात्रस्यशयानस्योपस्वेदनंप्रस्तरस्वेदइतिविद्यात्|[ii] | (Cha. Su. 14/42)
Type: Snigdha
In thisSveda, a mattress is prepared byspreadingŚūkaor ŚamīDhānya, Pulāka,Veśavāra(steamed boneless meat), Pāyasa(sweet porridge),Kṛśara(boiled mixture of pulses and cereals), and Utkārika(pudding cake)evenlyand cover itwithKauśeyaVastra, EraṇḍaPātraorArkaPatra. Thenthepatientwhohasproperlyanointedwithoilshould lie overthisand cover thebody withblankettillproperSvedanaoccurs.
Indications: –Pr̥ṣṭhaśūla,Pārśvaśūla, Kaṭīśūla, Gr̥dhrasī, KaṭīGraha
- NĀḌISVEDA
स्वेदनद्रव्याणांपुनर्मूलफलपत्रशुङ्गादीनांमृगशकुनपिशितशिरस्पदादीनामुष्णस्वभावानांवायथार्हमम्ललवणस्नेहोपसंहितानांमूत्रक्षीरादीनांवाकुम्भ्यांबाष्पमनुद्वमन्त्यामुत्क्वथितानांनाड्याशरेषीकावंशदलकरञ्जार्कपत्रान्यतमकृतयागजाग्रहस्तसंस्थानयाव्यामदीर्घयाव्यामार्धदीर्घयावाव्यामचतुर्भागाष्टभागमूलाग्रपरिणाहस्रोतसासर्वतोवातहरपत्रसंवृतच्छिद्रयाद्विस्त्रिर्वाविनामितयावातहरसिद्धस्नेहाभ्यक्तगात्रोबाष्पमुपहरेत्; बाष्पोह्यनृजुगामीविहतचण्डवेगस्त्वचमविदहन्सुखंस्वेदयतीतिनाडीस्वेदः[iii]| (Cha. Su. 14/43)
Drugs used for fomentation include Varuṇa,Guḍūci, Śigru, Mālatī, BṛhatPañcamūlaetc or animal-based articles (flesh and heads of animals and birds) are mixed up with sour, salt or unctuous substances and urine, milk, etc. and decocted in a pitcher in such a way that the vapour does not leak out. Then, a pipe made up of leaves of Vaṃśa, Karañja or Arka with its fore part having the shape of the trunk of an elephant is inserted into the pitcher. The pipe required should be of one vyāma(91.44cm) or half a Vyāma(45.72 cm) length, with its circumference being one-fourth of a Vyāma(22.86 cm) in its proximal end, one-eighth of a Vyāmain the distal end, and curved twice or thrice. All the clefts in the pipe should be well covered with leaves that alleviate Vāta. The well-massaged patient should then get this steam through the curved pipe. Curvatures of the pipe help in lessening the intensity of steam and thus help in providing a comfortable fomentation experience. This fomentation technique is called NāḍiSveda
Indications:-Vātapradhānaconditions, SandhigataVāta
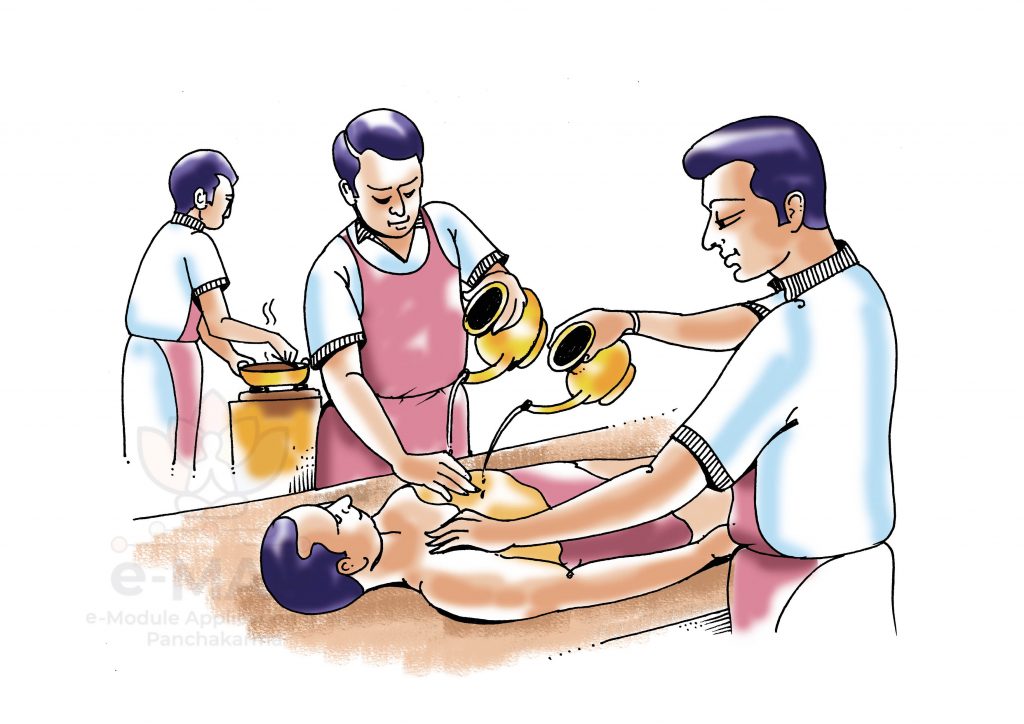
- PARIṢEKASVEDA
वातिकोत्तरवातिकानांपुनर्मूलादीनामुत्क्वाथैःसुखोष्णैःकुम्भीर्वर्षणिकाःप्रनाडीर्वापूरयित्वायथार्हसिद्धस्नेहाभ्यक्तगात्रंवस्त्रावच्छन्नंपरिषेचयेदितिपरिषेकः[iv] |
(Cha. Su. 14/44)
The procedure in which hot liquids (oil, decoction etc) are poured over the patient at a specific height is known as Pariṣeka.
Materials used
- Mūlādi(Patra, Phala) which alleviates Vāta , VātaKapha
- Decoction prepared with PatraBhaṅga(chopped leaves) of Śigru, Vāraṇaka, Eraṇḍa, Karañja, Surasa, Ārjaka, Śirīṣa, Vāsā, Vaṃśa, Arka, Mālatī, DīrghaVṛnta, Vacādi, ĀnūpavārijaMāṃsaand Daśamūla added with Ghṛta, Surā, Śukta, Vāri or Kṣīra
Instruments used
Kumbhi,Varṣaṇika, Pranāḍi
Method
- Decoction of the prescribed drugs is prepared and Luke warm decoction is filled into Kumbhi, VarṣaṇikaorPranāḍi.
- Then Pariṣekacan be performed after Abhyaṅga
- Cover the body with cloth during the procedure.
Indications:-Pittasaṃsṛṣṭa conditions, SandhigataVāta, Pakṣāghāta, Vātarakta, Skin diseases
- AVAGĀHASVEDA
वातहरोत्क्वाथक्षीरतैलघृतपिशितरसोष्णसलिलकोष्ठकावगाहस्तुयथोक्तएवावगाहः[v] |
(Cha. Su. 14/45)
- Immersion of the affected part in a tub filled with suitable warm VātāhāraKvātha, Kṣīra, Taila, Ghṛta, UṣṇaJala
- It can be carried out for full body in SarvāṅgaVyādhiand locally indiseases like Arśas, Mūtrākrichra.
- जलकोष्ठःअवगाहार्थकृतमहत्जलपात्रम्॥ (Cakrapāṇi)
According to Cakrapāṇi, Jalakoṣṭhais a large tub like vessel used for Avagāha
Method
- After Abhyaṅga, patient is asked to sit or lie down in the tub filled with liquid by keeping the head above.
- According to Bhāvaprakāśa, liquid level is 6 Aṅgulaabove Nābhi(naval)
- Duration of procedure – 1 Muhūrta
Indications:-Pr̥ṣṭhaśūla, ŚroṇiŚūla, Kaṭīśūla, Gr̥dhrasī, Asmari, Arśas
- JENTĀKASVEDA
तत्रपूर्वस्यांदिश्युत्तरस्यांवागुणवतिप्रशस्तेभूमिभागेकृष्णमधुरमृत्तिकेसुवर्णमृत्तिकेवापरीवापपुष्करिण्यादीनांजलाशयानामन्यतमस्यकूलेदक्षिणेपश्चिमेवासूपतीर्थेसमसुविभक्तभूमिभागेसप्ताष्टौवाऽरत्नीरुपक्रम्योदकात्प्राङ्मुखमुदङ्मुखंवाऽभिमुखतीर्थंकूटागारंकारयेत्, उत्सेधविस्तारतःपरमरत्नीःषोडश, समन्तात्सुवृत्तंमृत्कर्मसम्पन्नमनेकवातायनम्; अस्यकूटागारस्यान्तःसमन्ततोभित्तिमरत्निविस्तारोत्सेधांपिण्डिकांकारयेदाकपाटात्, मध्येचास्यकूटागारस्यचतुष्किष्कुमात्रंपुरुषप्रमाणंमृन्मयंकन्दुसंस्थानंबहुसूक्ष्मच्छिद्रमङ्गारकोष्ठकस्तम्भंसपिधानंकारयेत्; तंचखादिराणामाश्वकर्णादीनांवाकाष्ठानांपूरयित्वाप्रदीपयेत्; सयदाजानीयात्साधुदग्धानिकाष्ठानिगतधूमान्यवतप्तंचकेवलमग्निनातदग्निगृहंस्वेदयोग्येनचोष्मणायुक्तमिति,तत्रैनंपुरुषंवातहराभ्यक्तगात्रंवस्त्रावच्छन्नंप्रवेशयेत्, प्रवेशयंश्चैनमनुशिष्यात्- सौम्य! प्रविशकल्याणायारोग्यायचेति,प्रविश्यचैनांपिण्डिकामधिरुह्यपार्श्वापरपार्श्वाभ्यांयथासुखंशयीथाः, नचत्वयास्वेदमूर्च्छापरीतेनापिसतापिण्डिकैषाविमोक्तव्याऽऽप्राणोच्छ्वासात्, भ्रश्यमानोह्यतःपिण्डिवकावकाशाद्द्वारमनधिगच्छन्स्वेदमूर्च्छापरीततयासद्यःप्राणाञ्जह्याः, तस्मात्पिण्डिकामेनांनकथञ्चनमुञ्चेथाः; त्वंयदाजानीयाः- विगताभिष्यन्दमात्मानंसम्यक्प्रस्रुतस्वेदपिच्छंसर्वस्रोतोविमुक्तंलघूभूतमपगतविबन्धस्तम्भसुप्तिवेदनागौरवमिति, ततस्तांपिण्डिकामनुसरन्द्वारंप्रपद्येथाः, निष्क्रम्यचनसहसाचक्षुषोःपरिपालनार्थंशीतोदकमुपस्पृशेथाः, अपगतसन्तापक्लमस्तुमुहूर्तात्सुखोष्णेनवारिणायथान्यायंपरिषिक्तोऽश्नीयाः; इतिजेन्ताकस्वेदः[vi] |
(Cha. Su. 14/46)
Svedana prepared in a specially prepared Kuṭi is known as JentākaSveda.
Selection of Land
- Physician should examine the land before construction. Land should be selected in Eastern or Western side.
- Land should be fertile with proper mist, sunlight and the soil should be sweet, black or golden brown in colour.
- It should be on the southern or eastern bank of a water reservoir like small or a big pond.
- The level of land should be uniformly plain and it should be situated ata distance of 7-8 Aratniabout 12 feet from the reservoir.
Construction of building
- The height and diameter of the building should be 6 Aratni.
- The building should be uniformly circular, well plastered with mud and should have many windows to facilitate ventilation.
- A bench of one Aratniheight and one Aratniwidth is then to be prepared call around the wall up to the door.
- An oven of clay should be prepared in the centre of the room.Its diameter should be 4Hastaand height should be equal to the height of the individual. It should be circular in shape and should have fine holes and lid.
- It should be filled with the fuel of Khadira and Aśvakarṇashould be ignited.
When the physician is sure that the fuel is well burnt and the smoke has completely disappeared, the room is heated by the fire and heat is enough to produce fomentation, then ask the patient to enter the room.
Preparation of patient
- Before entering the room, the patient should be well massaged with VātāhāraTailas and covered with a cloth.
- Advice the patient that do not leave the bench if he feels fainting during the procedure as it may not be possible for him to reach the door.
PaścātKarma
- When the person feels he is free from all obstructions the sweat along with its sticking portion is completely drained out, all channels are light and free from obstructions, there is no stiffness, numbness, pain, heaviness then he should move towards the door.
- One should not sprinkle cold water to eyes after coming out as it may affect eyes.
- After heat and exertion are over he should take bath with Luke warm water after one Muhūrta. Then he should be asked to consume LaghuĀhāra.
- AŚMAGHANASVEDA
शयानस्यप्रमाणेनघनामश्ममयींशिलाम्| तापयित्वामारुतघ्नैर्दारुभिःसम्प्रदीपितैः|
व्यपोज्झ्यसर्वानङ्गारान्प्रोक्ष्यचैवोष्णवारिणा| तांशिलामथकुर्वीतकौषेयाविकसंस्तराम् |
तस्यांस्वभ्यक्तसर्वाङ्गःस्वपन्स्विद्यतिनासुखम्| कौरवाजिनकौषेयप्रावाराद्यैःसुसंवृतः | इत्यक्तोऽश्मघनस्वेदः[vii]| (Cha. Su. 14/48)
This is a kind of fomentation where the fomentation is induced by making the person to lie down over a preheated slab of stone.
Materials required
- Compact slab of stone measuring the length of a man
- Fuels having Vātāhāra property
- Silk/woollen clothes
Method
- Firewood having Vātāhāra properties should be burned over a compact slab of stone.
- When stone gets heated firewood should be removed and hot water should be sprinkled over the slab.
- Stone should be covered with woollen cloth
- Person who has undergone SarvangaAbhyaṅga should be on the stone and should be covered with a sheet
- Patient should lie down till proper Svedana occurs.
- KARṢŪSVEDA
कर्षूस्वेदःप्रवक्ष्यते| खानयेच्छयनस्याधःकर्षूंस्थानविभागवित् |
दीप्तैरधूमैरङ्गारैस्तांकर्षूंपूरयेत्ततः| तस्यामुपरिशय्यायांस्वपन्स्विद्यतिनासुखम्[viii] |
(Cha. Su. 14/51)
- Karṣū means a pit containing a large space inside and a narrow opening at the top.
- For this type of Sveda, a circular pit is dug and is filled with smokeless burning coal
- A cot covered with KauśeyaVastrais spread on it.
- The patient after proper Abhyaṅga is asked to lie down on the cot by covering the body with bed sheet till he gets good perspiration along with other symptoms of proper Svedana.
- KUṬISVEDA
अनत्युत्सेधविस्तारांवृत्ताकारामलोचनाम्| घनभित्तिंकुटींकृत्वाकुष्ठाद्यैःसम्प्रलेपयेत् |
कुटीमध्येभिषक्शय्यांस्वास्तीर्णामुपकल्पयेत्| प्रावाराजिनकौशेयकुथकम्बलगोलकैः |
हसन्तिकाभिरङ्गारपूर्णाभिस्तांचसर्वशः| परिवार्यान्तरारोहेदभ्यक्तःस्विद्यतेसुखम्[ix] |
(Cha. Su. 14/52)
- Kuṭishould be construed which is not too high and not too wide.
- It should be round in shape with no windows. The inner wall of the hut should be plastered with Kuṣṭhādi drugs
- In the centre of the hut a bed covered with cotton, silk, deer skin, wollen should be placed.
- The bed should be surrounded with the furnace
- The patient who has taken Abhyaṅga is asked to lie down on the cot by covering his body with a silk cloth till he gets perspiration.
- BHŪSVEDA
यएवाश्मघनस्वेदविधिर्भूमौसएवतु| प्रशस्तायांनिवातायांसमायामुपदिश्यते[x] |
(Cha. Su. 14/55)
The procedure same as AśmaghanaSveda. In AśmaghanaSveda a stone slab is used while in BhūSveda the same process is done on ground.
- KUMBHĪSVEDA
कुम्भींवातहरक्वाथपूर्णांभूमौनिखानयेत्| अर्धभागंत्रिभागंवाशयनंतत्रचोपरि |
स्थापयेदासनंवाऽपिनातिसान्द्रपरिच्छदम्| अथकुम्भ्यांसुसन्तप्तान्प्रक्षिपेदयसोगुडान् |
पाषाणान्वोष्मणातेनतत्स्थःस्विद्यतिनासुखम्| सुसंवृताङ्गःस्वभ्यक्तःस्नेहैरनिलनाशनैः[xi] |
(Cha. Su. 14/56)
A pot filled with VātāhāraKaṣāya is taken and buried in the earth upto the level of neck of pot. A cot should be placed over the pot and the patient who has anointed with oil should lie on it and cover the body with blanket. Then red hot iron bolus is put into the pot and the steam comes out from the pot.
- HOLĀKASVEDA
धीतीकांतुकरीषाणांयथोक्तानांप्रदीपयेत्| शयनान्तःप्रमाणेनशय्यामुपरितत्रच |
सुदग्धायांविधूमायांयथोक्तामुपकल्पयेत्| स्ववच्छन्नःस्वपंस्तत्राभ्यक्तःस्विद्यतिनासुखम् |
होलाकस्वेदइत्येषसुखःप्रोक्तोमहर्षिणा| इतित्रयोदशविधःस्वेदोऽग्निगुणसंश्रयः[xii] |
(Cha. Su. 14/61)
A long tank measuring 6ft* 2 ft is made on the earth surface. Then fill it with dung of animals and burn it. When becomes free from smoke, a cot is kept over the tank, patient who has anointed with oil should lie on it and cover the body with the blanket till SamyakSvinnaLakṣaṇa are seen.
- KŪPASVEDA
कूपंशयनविस्तारंद्विगुणंचापिवेधतः| देशेनिवातेशस्तेचकुर्यादन्तःसुमार्जितम् |
हस्त्यश्वगोखरोष्ट्राणांकरीषैर्दग्धपूरिते| स्ववच्छन्नःसुसंस्तीर्णेऽभ्यक्तःस्विद्यतिनासुखम्[xiii] |
(Cha. Su. 14/59)
Long pit is made and then fill the pit with dung of animals and burn it. When smoke stops, a cot is kept over the pit. Patient who has anointed with oil should lie on it and cover the body with blanket till SamyaksvinnaLakṣaṇa are obtained.
[i] Cha.Su.14/25
[ii] Cha.Su.14/42
[iii] Cha.Su.14/43
[iv] Cha.Su.14/44
[v] Cha.Su.14/45
[vi] Cha.Su.14/46
[vii] Cha.Su.14/48
[viii] Cha.Su.14/51
[ix] Cha.Su.14/52
[x] Cha.Su.14/55
[xi] Cha.Su.14/56
[xii] Cha.Su.14/61
[xiii] Cha.Su.14/59
व्यायामउष्णसदनंगुरुप्रावरणंक्षुधा|
बहुपानंभयक्रोधावुपनाहाहवातपाः|
स्वेदयन्तिदशैतानिनरमग्निगुणादृते |
(Cha.Su.14/64)
Ten types of anagneyaSveda are Vyāyāma, UṣṇaSadana,GuruPrāvaraṇa,Kṣudhā, Bahupāna, Bhaya, Upanāha, Krōdha, Āhava,Ātapa.
Utility
स्वेदोहितस्त्वनाग्नेयोवातेमेदःकफावृते| (A. H.Su. 17/28)
NiragniSvedas indicated in KaphaMedāvṛtaVāta disorders.



