
UG Module 6 - Lesson 2
BASTI KARMA
EXPLANATORY NOTES
The apparatus used for the administration of Basti is called as Basti Yantra. It consists of two parts:
1) Basti Netra
2) Basti Puṭaka
BASTI NETRA
तयोस्तु नेत्रं हेमादिधातुदार्वस्थिवेणुजम् ||
गोपुच्छाकारमच्छिद्रं श्लक्ष्णर्जु गुलिकामुखम् | (A. H. Su. 19/9)
Material used in formation of Basti Netra is gold , silver and other metals, bones of animals, wooden, bamboo. It should be straight and conical shape like cow’s tail, without any holes, the edges of the tip are smooth and size of Gulikā.
सुवर्णरूप्यत्रपुताम्ररीतिकांस्यास्थिशस्त्रद्रुमवेणुदन्तैः [१] |
नलैर्विषाणैर्मणिभिश्च तैस्तैर्नेत्राणि कार्याणि सु(त्रि)कर्णिकानि [२] || (Cha. Si. 3/7)
The Basti Netra is made either from gold, silver, tin, copper, bronze, bone, iron, wood, bamboo, ivory, pipe, horn or gems. It has three ear like projections called Karṇikās.
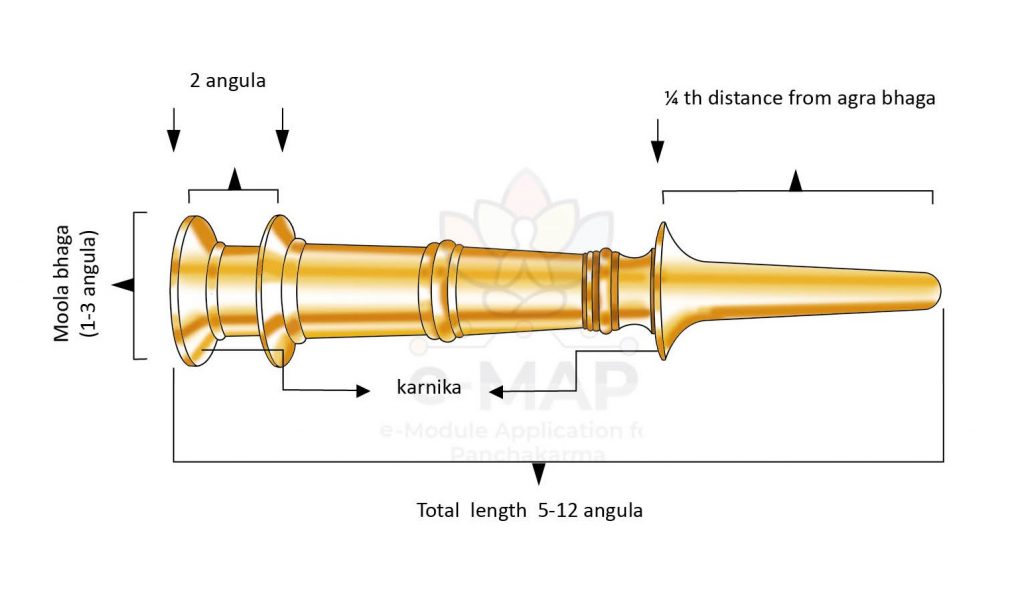
Netra Pramāna
ऊनेऽब्दे पञ्च, पूर्णेऽस्मिन्नासप्तभ्योऽङ्गुलानि षट्||
सप्तमे सप्त, तान्यष्टौ द्वादशे, षोडशे नव|
द्वादशैव परं विंशाद्वीक्ष्य वर्षान्तरेषु च||
वयोबलशरीराणि प्रमाणमभिवर्द्धयेत् (A. H. Su. 19/10-11)
The length varies from 5 to 12 Aṅgula according to age. For below one year, size of Basti Netra is 5 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of wild green gram. For 1 year, size of Basti Netra is 6 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of green gram. For 7 years, size of Basti Netra is 7 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of black gram. For 12 years, size of Basti Netra is 8 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of a pea. For 16 years, size of Basti Netra is 9 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of soaked pea. For 20 years, size of Basti Netra is 12 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of Jujuba seed. The size of the nozzle can be increased depending upon the age, strength and the physique of the patient.
Mūla and Agra Chidra Pramāna
स्वाङ्गुष्ठेन समं मूले स्थौल्येनाग्रे कनिष्ठया| (A. H. Su. 19/12)
The circumference of the base and the tip should be the circumference of thumb and little finger respectively.
पूर्णेऽब्देऽङ्गुलमादाय तदर्द्धार्द्धप्रवर्द्धितम्|
त्र्यङ्गुलं परमं छिद्रं मूलेऽग्रे वहते तु यत्||१३||
मुद्गं माषं कलायं च क्लिन्नं कर्कन्धुकं क्रमात्| (A.Hr.Su.19/13-14)
Age | Length of the Netra | Size of the tip |
1 year | 5 Aṅgula | Mudgavāhi |
6 years | 6 Aṅgula | Mudgavāhi |
7 years | 7 Aṅgula | Māṣavāhi |
12 years | 8 Aṅgula | Kalāyavāhi |
16 – 19 years | 9 Aṅgula | Klinna Kalāyavāhi |
20 years | 12 Aṅgula | Karkandhuvāhi |
मूलाच्छिद्रप्रमाणेन प्रान्ते घटितकर्णिकम्||
वर्त्याऽग्रे पिहितं, मूले यथास्वं ह्यङ्गुलान्तरम्|
कर्णिकाद्वितयं नेत्रे कुर्यात्——————–| (A. H. Su. 19/14-15)
Near the orifice at the base of Basti Netra, a Karṇikā (ear like ridge) of the same size of the orifice should be made. Another second Karṇikā should be made at a distance of 2 Aṅgula from the first Karṇikā. The tip of Basti Netra should be closed with a piece of cotton.
षड्द्वादशाष्टाङ्गुलसम्मितानि षड्विंशतिद्वादशवर्षजानाम्|
स्युर्मुद्गकर्कन्धुसतीनवाहिच्छिद्राणि वर्त्याऽपिहितानि चैव||८||
यथावयोऽङ्गुष्ठकनिष्ठिकाभ्यां मूलाग्रयोः स्युः परिणाहवन्ति|
ऋजूनि गोपुच्छसमाकृतीनि श्लक्ष्णानि च स्युर्गुडिकामुखानि||९||
स्यात् कर्णिकैकाऽग्रचतुर्थभागे मूलाश्रिते बस्तिनिबन्धने द्वे| (Cha.Si.3/10)
Age | Size | Per year | Inner circumference of the tip |
1-6 years | 6 Aṅgula | Constant/no increase | Mudgavāhi |
7-12 years | 8 Aṅgula | Increased by 1/3 Aṅgula | Karkandhuvāhi |
13- 20 years | 12 Aṅgula | Increased by 1/2 Aṅgula | Satīnavāhi |
The outer circumference of the Netra at the base and the inner circumference at the tip should be same as that of the thumb and little finger respective of the age of the patient. The Netra should be straight and Gopucchasamākriti. The opening at the tip should be Ślakṣṇa, and Gudikāmukhi (globular). Among the three Karṇikās, one Karṇikā is fixed at the level of 1/4th from the tip and two other Karṇikās are fixed at the base for Bandhana of the Puṭaka around the nozzle.
तत्र सांवत्सरिकाष्टद्विरष्टवर्षाणां षडष्टदशाङ्गुलप्रमाणानि कनिष्ठिकानामिकामध्यमाङ्गुलिपरिणाहान्यग्रेऽध्यर्धाङ्गुलद्व्यङ्गुलार्धतृतीयाङ्गुलसन्निविष्टकर्णिकानि कङ्कश्येनबर्हिणपक्षनाडीतुल्यप्रवेशानि मुद्गमाषकलायमात्रस्रोतांसि विदध्यान्नेत्राणि |तेषु चास्थापनद्रव्यप्रमाणमातुरहस्तसम्मितेन प्रसृतेन सम्मितौ प्रसृतौ द्वौ चत्वारोऽष्टौ च विधेयाः || वर्षान्तरेषु नेत्राणां बस्तिमानस्य चैव हि |वयोबलशरीराणि समीक्ष्योत्कर्षयेद्विधिम् || पञ्चविंशतेरूर्ध्वं द्वादशाङ्गुलं, मूलेऽङ्गुष्ठोदरपरीणाहम्, अग्रे कनिष्ठिकोदरपरीणाहम्, अग्रे त्र्यङ्गुलसन्निविष्टकर्णिकं, गृध्रपक्षनाडीतुल्यप्रवेशं, कोलास्थिमात्रछिद्रं, क्लिन्नकलायमात्रछिद्रमित्येके; सर्वाणि मूले बस्तिनिबन्धनार्थं द्विकर्णिकानि |आस्थापनद्रव्यप्रमाणं तु विहितं द्वादशप्रसृताः |
सप्ततेस्तूर्ध्वं नेत्रप्रमाणमेतदेव, द्रव्यप्रमाणं तु द्विरष्टवर्षवत् || ( Su.Chi.35/7-9)
Age | Size | Diameter of Mūla Bhāga | Diameter of Mūlabhāga Chidra | Diameter of Agrabhāga Chidra | Karṇikā |
1 year | 6 Aṅgula | Kaniṣṭikā Samāna | Kaṅka Pakṣi Nādi Samāna | Mudgavāhi | 1 ½ Aṅgula from Agrabhāga |
8 years | 8 Aṅgula | Anāmika Samāna | Syena Pakṣi Nādi Samāna | Mashavāhi | 2 Aṅgula from Agrabhāga |
16 years | 10 Aṅgula | Madhyama Aṅguli Samāna | Madhyama Aṅguli Samāna | Kalāyavāhi | 2 ½ Aṅgula from Agrabhāga |
25 years | 12 Aṅgula | Aṅguṣṭha Samāna | Aṅguṣṭha Samāna | Aṅkurita Kalāyavāhi | 3 Aṅgula from Agrabhāga |
पूर्णेऽब्देऽङ्गुलमादाय तदर्द्धार्द्धप्रवर्द्धितम्|
त्र्यङ्गुलं परमं छिद्रं मूलेऽग्रे वहते तु यत्||१३||
मुद्गं माषं कलायं च क्लिन्नं कर्कन्धुकं क्रमात्| (A.Hr.Su.19/13-14)
Age | Length of the Netra | Size of the tip |
1 year | 5 Aṅgula | Mudgavāhi |
6 years | 6 Aṅgula | Mudgavāhi |
7 years | 7 Aṅgula | Māṣavāhi |
12 years | 8 Aṅgula | Kalāyavāhi |
16 – 19 years | 9 Aṅgula | Klinna Kalāyavāhi |
20 years | 12 Aṅgula | Karkandhuvāhi |
BASTI PUṬAKA
- जारद्गवो माहिषहारिणौ वा स्याच्छौकरो बस्तिरजस्य वाऽपि||१०||
दृढस्तनुर्नष्टसिरो विगन्धः कषायरक्तः सुमृदुः सुशुद्धः| (Cha.Si. 3/10-11) - अजाविमहिषादीनां बस्तिं सुमृदितं दृढम्|
कषायरक्तं निश्छिद्रग्रन्थिगन्धशिरं तनुम्||१६|| (A.Hr.Su.19/16-17)
Basti Puṭaka is made from the bladder of animals such as old cow, buffalo, deer, goat, pig, etc. as per the size required. In unavailability of urinary bladder leg skin of aquatic birds or thick cloth can be used.
FEATURES OF BASTI PUṬAKA
The Basti Puṭaka should be stable, thin, free from vessels and without any foul odour. It should be processed with Kaṣāya by which it becomes red in colour. It should be very soft and very clean. It should not have holes and any other opening for leakage, should not contain nodules.
BASTI NETRA DOṢĀS AND ITS VYĀPATS
- ह्रस्वं दीर्घं तनु स्थूलं जीर्णं शिथिलबन्धनम्|
पार्श्वच्छिद्रं तथा वक्रमष्टौ नेत्राणि वर्जयेत्||४||
अप्राप्त्यतिगतिक्षोभकर्षणक्षणनस्रवाः|
गुदपीडा गतिर्जिह्मा तेषां दोषा यथाक्रमम्|| (Cha.Si.5/4-5) - अतिस्थूलं, कर्कशम्, अवनतं, अणुभिन्नं, सन्निकृष्टविप्रकृष्टकर्णिकं, सूक्ष्मातिच्छिद्रम्,
अतिदीर्घम्, अतिह्रस्वम्, अस्रिमदित्येकादश नेत्रदोषाः (Su.chi.37/32)
Netra Doṣa | Vyāpats |
Hrasva | Aprāpti |
Dīrgha | Ati Gati |
Tanu | Kṣobha |
Sthūla | Karṣana |
Jīrṇa | Kṣanana |
Śithilabandhana | Srāva |
Pārśvachidra | Guda Pīda |
Vakra | Gatijihma |
Karkaśa | |
Avannata | |
Aṇubhinna | |
Sannikriṣta Karṇikā | |
Viprakriṣta Karṇikā | |
Sūkṣma Chidra | |
Ati Chidra | |
Asrima |
BASTI PUṬAKA DOṢĀS AND ITS VYĀPATS
- बहलता, अल्पता, सच्छिद्रता, प्रस्तीर्णता, दुर्बद्धतेति पञ्च बस्तिदोषाः || ( Su.chi.37/32)
- विषममांसलच्छिन्नस्थूलजालिकवातलाः|
स्निग्धः क्लिन्नश्च तानष्टौ बस्तीन् कर्मसु वर्जयेत्||६||
गतिवैषम्यविस्रत्वस्रावदौर्ग्राह्यनिस्रवाः|
फेनिलच्युत्यधार्यत्वं बस्तेः स्युर्बस्तिदोषतः|| (Cha.Si.5/6-7)
Puṭaka Doṣās | Vyāpats |
Viṣama | Gati Vaiṣamya |
Māṃsala | Visratva |
Chidra | Srāva |
Sthūla | Daurgrāhya |
Jalikā | Nisrāva |
Vātala | Phenila |
Snigdha | Cyuta |
Klinna | Adhāryatva |
Bahalata | |
Alpata | |
Sachidra | |
Prastirna | |
Durbadha |
MODIFIED BASTI NETRA
SL No | Modified Basti Netra | Merits and Demerits |
1 | Plastic Basti Netra | • It is easy to use •It is washable and reusable •Cost effective •It is available in different sizes |
2 | Rubber catheters Different size catheters are available in the market, commonly number 12 size for elders and 8 size for paediatric age group is used. | • It is available in different sizes •Rubber catheter can be used for a single use and then disposed •By using rubber catheter one can give high rectal or low rectal enema •Less chance of injury and complications |
3 | Glycerine syringe Used for the administration of Anuvāsana Basti. | • Economical •Easy to use and disposable. •These have less chance of infection. |
MODIFIED BASTI PUṬAKA
SL No | Modified Basti Puṭaka | Merits and Demerits |
1 | Enema Can The measuring cans attached with the pipe are now a days used for the administration of Nirūha Basti. Either the tip of the pipe or the end of the pipe attached with a catheter of suitable size and is inserted into the anal canal. | • Easily available and easy to administer •No need of expertisation •Chances of complications like Savāta Basti is very less •It is easy for cleaning Demerits Dravya moves down by gravity and so administration of Dravya with pressure doesn’t happen |
2 | Plastic /Rubber Basti Yantra as Puṭaka for Nirūha This Yantra is made from one piece surgical plastic | • It is transparent and sterilisable and comes with rounded tip for painless insertion •Transparent body allows viewing of air in Basti material •It is easily available •Devoid of complications |
3 | Enema Syringe This has a stainless steel body with bronze head or delrin head. The disposable Basti tip is screwed to the head. These are available in the 100ml/250 ml sizes for Mātra Basti and Anuvāsana Basti. The tips are also available in two sizes- adult and paediatric | • It is easily available •Devoid of complications •This tip has an ideal hole size for Ayurvedic use. •Easy for cleaning •Simple to administer |
IMPORTANT SLOKA
तयोस्तु नेत्रं हेमादिधातुदार्वस्थिवेणुजम् ||
गोपुच्छाकारमच्छिद्रं श्लक्ष्णर्जु गुलिकामुखम् | (AH. Su. 19/9)
Material used in formation of Basti Yantra is gold , silver and other metals, bones of animals, wooden, bamboo. It should be straight and conical shape like cow’s tail, without any holes, the edges of the tip are smooth and size of Gulikā
ऊनेऽब्दे पञ्च, पूर्णेऽस्मिन्नासप्तभ्योऽङ्गुलानि षट्||
सप्तमे सप्त, तान्यष्टौ द्वादशे, षोडशे नव|
द्वादशैव परं विंशाद्वीक्ष्य वर्षान्तरेषु च||
वयोबलशरीराणि प्रमाणमभिवर्द्धयेत् (AH. Su. 19/10-11)
The length varies from 5 to 12 Aṅgula according to age. For below one year, size of Basti Netra is 5 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of wild green gram. For 1 year, size of Basti Netra is 6 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of green gram. For 7 years, size of Basti Netra is 7 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of black gram. For 12 years, size of Basti Netra is 8 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of a pea. For 16 years, size of Basti Netra is 9 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of soaked pea. For 20 years, size of Basti Netra is 12 Aṅgula length and circumference of the tip is size of Jujuba seed. The size of the nozzle can be increased depending upon the age, strength and the physique of the patient.
स्वाङ्गुष्ठेन समं मूले स्थौल्येनाग्रे कनिष्ठया| (AH. Su. 19/12)
The circumference of the base and the tip should be the circumference of thumb and little finger respectively.
पूर्णेऽब्देऽङ्गुलमादाय तदर्द्धार्द्धप्रवर्द्धितम्|
त्र्यङ्गुलं परमं छिद्रं मूलेऽग्रे वहते तु यत्||
मुद्गं माषं कलायं च क्लिन्नं कर्कन्धुकं क्रमात्| (AH. Su. 19/13)
The circumference of the base is 1 Aṅgula for 1 year and half Aṅgula can be increased with age. The maximum circumference can go up to 3 Aṅgula. The tip of the Netra should permit mudga, masha, kalaya, klinna kalaya, karkandu and klinna karkandu respectively.
मूलाच्छिद्रप्रमाणेन प्रान्ते घटितकर्णिकम्॥
वर्त्याऽग्रे पिहितं, मूले यथास्वं द्वयङ्गुलान्तरम्।
कर्णिकाद्वितयं नेत्रे कुर्यात्——————–। (AH.Su.19/14-15)
Near the orifice at the base of Basti Netra, a Karṇikā (ear like ridge) of the same size of the orifice should be made. Another second Karṇikā should be made at a distance of 2 Aṅgula from the first Karṇikā. The tip of Basti Netra should be closed with a piece of cotton.
ह्रस्वं दीर्घं तनु स्थूलं जीर्णं शिथिलबन्धनम् |
पार्श्वच्छिद्रं तथा वक्रमष्टौ नेत्राणि वर्जयेत् ||
अप्राप्त्यतिगतिक्षोभकर्षणक्षणनस्रवाः|
गुदपीडा गतिर्जिह्मा तेषां दोषा यथाक्रमम् || (Ch. Si. 5/4-5)
The eight types of Netra Doṣās and the complications arising out of their use are Hrasva (shorter in size) which produce Aprāpti (enema fluid not reaching its destination), Dīrgha (longer in size) which produce Atigati (enema fluid penetrating far above), Tanu (thinner in shape) which produce Kṣobha (irritation in the rectum), Sthūla (thicker in shape) which produce Karṣana (bruising the wall of rectum), Jīrṇa (worn out) which produce Kṣanana (causing injury to the rectum), Śithilabandhana (loose fixation) which produce Srāva (leaking out of enema fluid), Pārśvachidra (having holes in the side) which produce Guda Pīda (pain in the rectum) and Vakra (curved) which produce Jihma Gati (tortuous passage of the fluid).
—————————-तत्र च योजयेत् ||
अजाविमहिषादीनां बस्तिं सुमृदितं दृढम् |
कषायरक्तं निश्छिद्रग्रन्थिगन्धशिरं तनुम् ||
ग्रथितं साधु सूत्रेण सुखसंस्थाप्यभेषजम् |
बस्त्यभावेऽङ्कपादं वान्यसेद्वासोऽथवा घनम् || (AH. Su. 19/15-16)
For Basti Puṭaka, urinary bladder of buffalo, deer, pig or goat should be used. It should be soft and stable, should be processed with Kaṣāya Dravyas, should not have holes and any other opening for leakage, should not contain nodules, should be odorless and thin. The Basti Puṭaka should be tied properly to the Basti Netra with a thread after filling Auṣadhī to the Puṭaka. In unavailability of urinary bladder leg skin of aquatic birds or thick cloth can be used.
विषममांसलच्छिन्नस्थूलजालिकवातलाः|
स्निग्धः क्लिन्नश्च तानष्टौ बस्तीन् कर्मसु वर्जयेत् ||
गतिवैषम्यविस्रत्वस्रावदौर्ग्राह्यनिस्रवाः|
फेनिलच्युत्यधार्यत्वं बस्तेः स्युर्बस्तिदोषतः|| (Ch. Si. 5/6-7)
The eight types of Bastis which are not to be used for the administration of enema and the complications arising out of their use are Viṣama (irregular in shape) which produce Gati Vaiṣamya (irregular flow of enema fluid), Māṃsala (fleshy) which produce Visratva (making the enema fluid smell fleshy), Chidra (torn) which produce Srāva (leakage of the fluid), Sthūla (thick) which produce Daurgrāhya (difficulty in handling), Jalikā (having network of small perforations) which produce Nisrāva (exudation of enema fluid from the receptacle), Vātala (having air bubbles inside) which produce Phenila (frothiness of fluid), Ati Snigdha (excessively unctuous) which produce Cyuti (slipping away of the receptacle) and Klinna (putrified) which produce Adhāryatva (inability to hold the receptacle).



